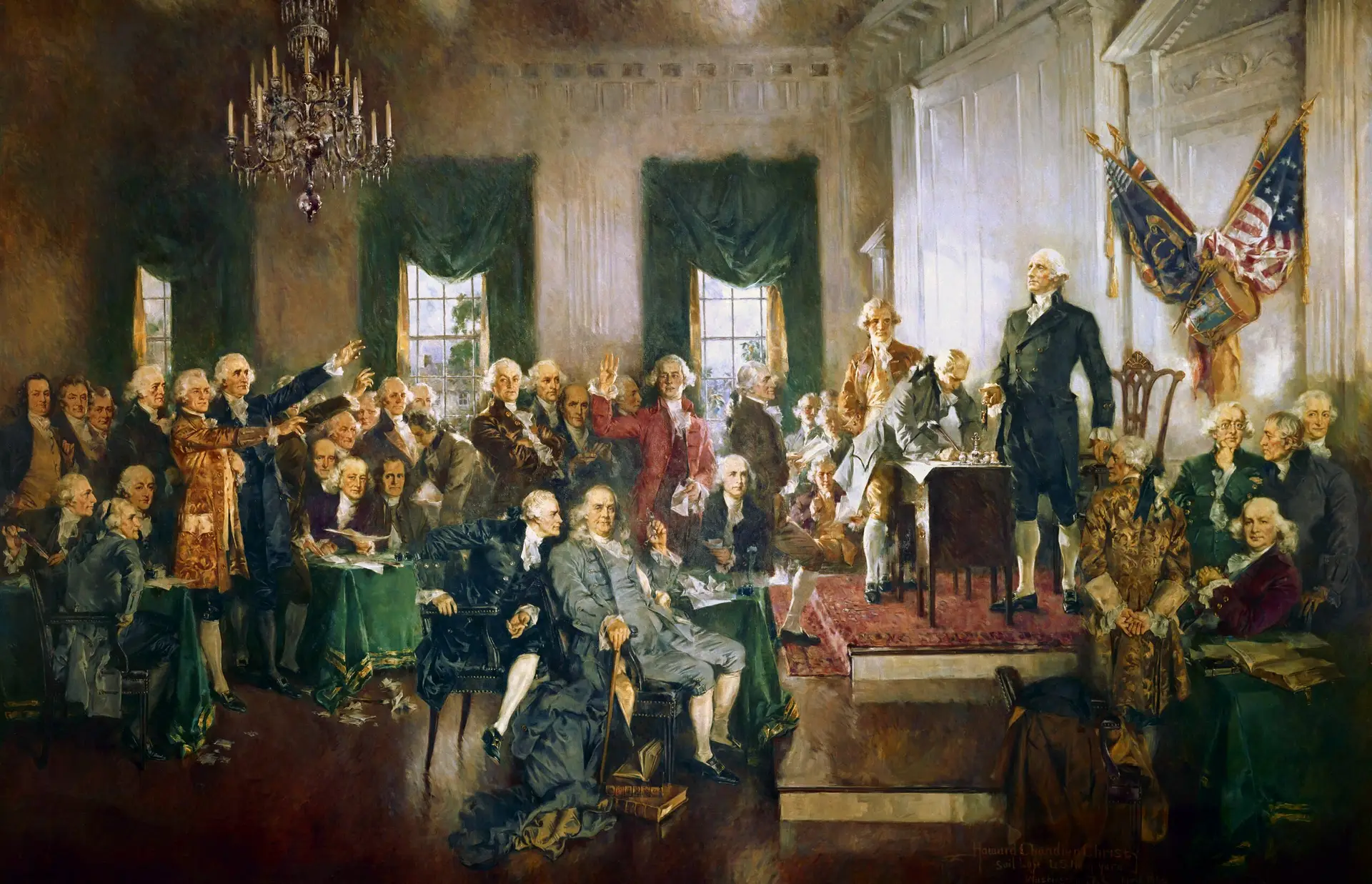

Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (Wiki Image).
Introduction
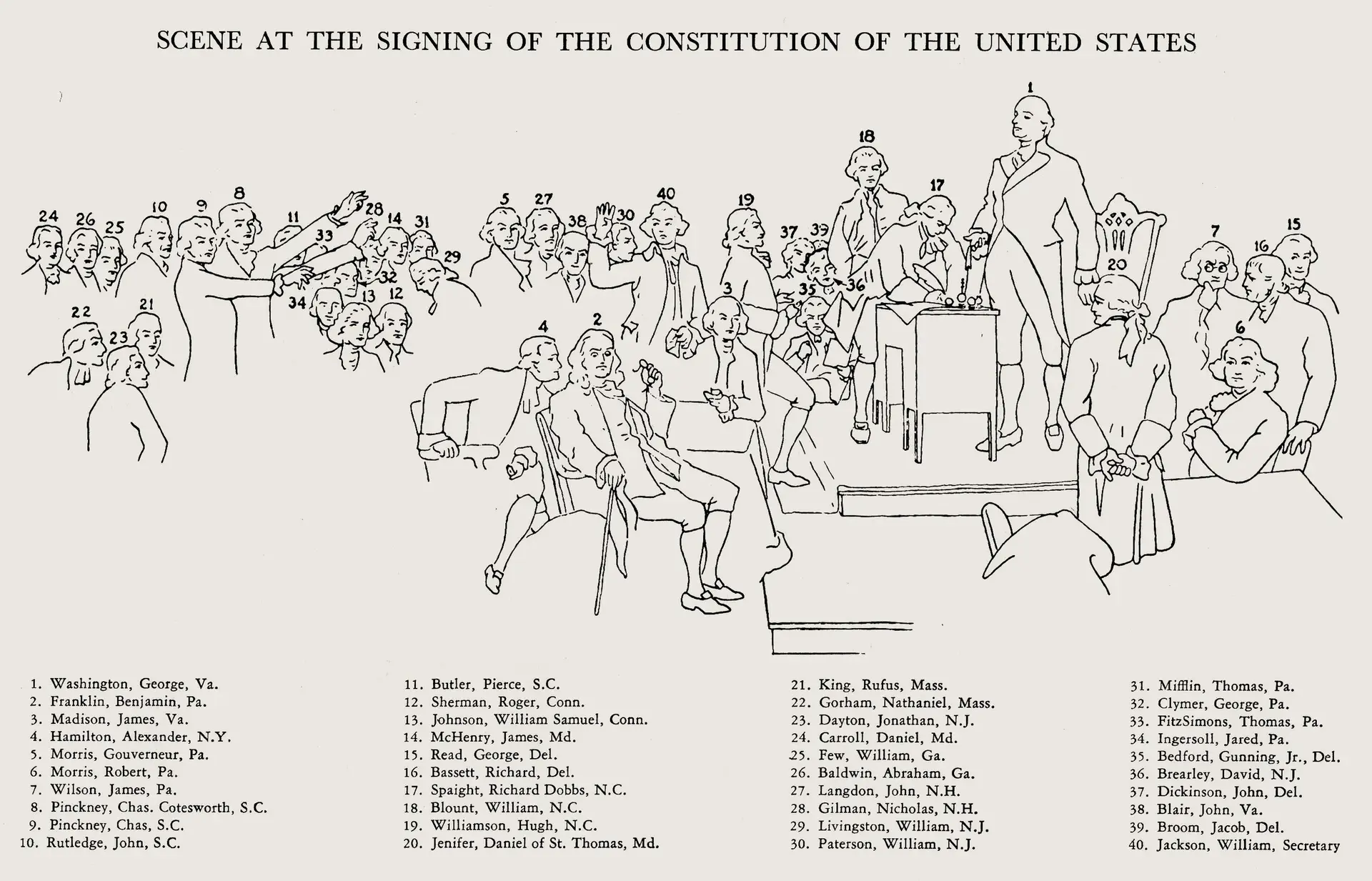
Key to figures in the painting (Wiki Image).
A.I. Washington, George, Va., faced obstacles, successes, wisdom, and Constitution leadership concerning the Constitution.

George Washington (Wiki image).
Yes, George Washington faced many obstacles, successes, wisdom, and Constitution leadership concerning the Constitution. Here are some of them:
Obstacles
- Washington faced opposition from delegates who wanted to create a strong central government.
- He was also a critic of slavery, but he was unable to convince the Convention to abolish it.
- Washington was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Washington was elected unanimously as the first President of the United States.
- He presided over the Constitutional Convention and helped to secure the ratification of the Constitution.
- He established many of the traditions and procedures of the presidency, which are still used today.
Wisdom
- Washington understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was a master of persuasion and was able to win over the support of his colleagues.
Constitution leadership
- Washington was a strong and effective leader during the Constitutional Convention. He helped to keep the Convention on track and to ensure that the delegates reached an agreement.
- He was also a strong advocate for the Constitution. He traveled to different parts of the country to speak in favor of the Constitution and to encourage people to ratify it.
- As President, Washington was a wise and decisive leader. He helped to establish the United States as a respected nation in the world, and he helped to protect the young republic from threats, both foreign and domestic.
Washington’s wisdom, foresight, persuasive skills, experience, and leadership were essential to the success of the Constitutional Convention and the early years of the United States. He was a true Founding Father, and his contributions to the country are still felt today.
Here is a specific example of Washington’s leadership during the Constitutional Convention:
- When the delegates were deadlocked over the issue of representation in the Senate, Washington stepped in and helped to break the deadlock. He said, “We must all agree to give up something in order to reach an agreement.” The delegates agreed, and the deadlock was finally broken.
Washington’s leadership helped to create a Constitution that was acceptable to all the delegates and that has served the United States well for over 200 years.
A.I. Franklin, Benjamin, Pa., faced obstacles, successes, wisdom, and wit concerning the Constitution.

Benjamin Franklin (Wiki Image).
Yes, Benjamin Franklin faced many obstacles, successes, wisdom, and wit concerning the Constitution.
Obstacles
- Franklin faced opposition from delegates who wanted to create a strong central government.
- He was also a critic of slavery, but he was unable to convince the Convention to abolish it.
- Franklin was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Franklin was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Franklin was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Franklin understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was a master of persuasion and was able to win over the support of his colleagues.
Wit
- Franklin was known for his wit and humor, which he often used to defuse tense situations at the Convention.
- He once proposed a compromise that would have created a bicameral legislature with one house elected by the people and the other house elected by the state legislatures. He called this compromise the “grand bargain,” and it was eventually adopted by the Convention. The grand bargain solved this disagreement by creating a two-house legislature, with the House of Representatives based on population and the Senate based on equal representation for each state.
Franklin’s wisdom, wit, and perseverance were essential to the success of the Constitutional Convention. He was a true Founding Father, and his contributions to the Constitution are still felt today.
Here is a specific example of Franklin’s wit and humor:
- When the delegates were deadlocked over the issue of representation in the Senate, Franklin suggested that they draw straws to break the tie. He said, “We have been six days debating this matter, and it appears that we have not yet come to an agreement. So, I suggest that we draw straws. The man who draws the shortest straw will have his way.” The delegates laughed, and the deadlock was finally broken.
Franklin’s wit and humor helped to create a more congenial atmosphere at the Convention, which was essential for the success of the drafting process.
In conclusion, Franklin faced many obstacles in his quest to help create a Constitution that would unite the states and protect the rights of all Americans. However, he was able to overcome these obstacles through his wisdom, foresight, persuasive skills, and wit. He was a true Founding Father, and his contributions to the Constitution are still felt today.
A.I. Madison, James, Va., faced obstacles, successes, wisdom, and The Federalist Papers concerning the Constitution.
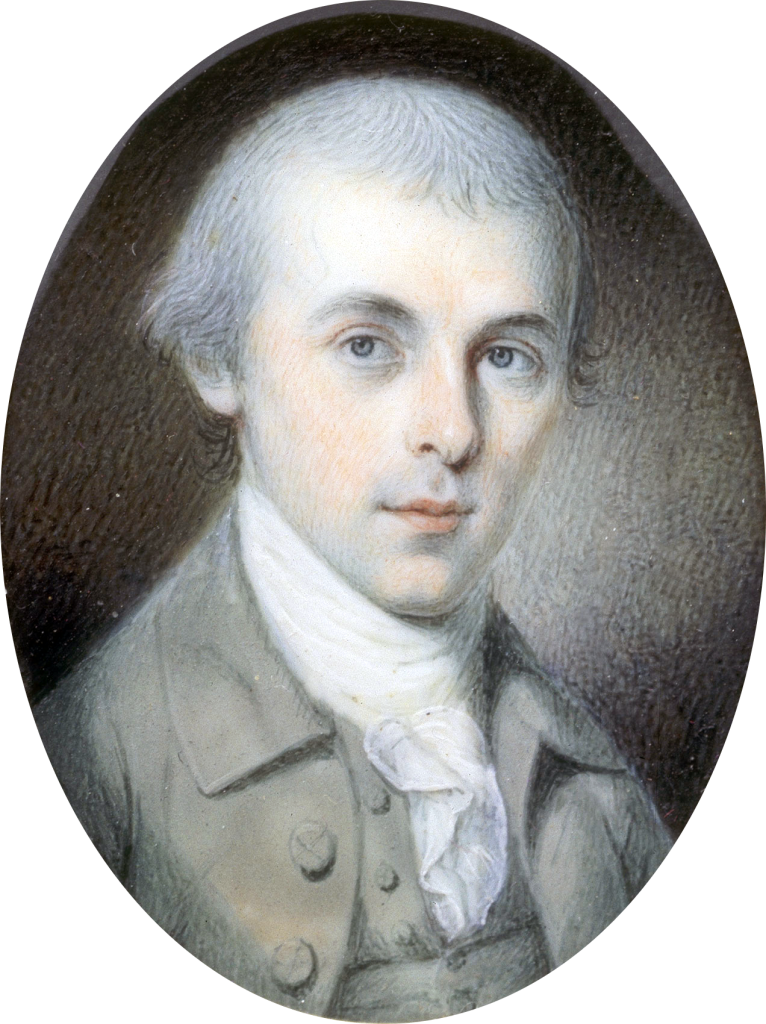

Madison’s portrait as Congressional delegate at age 32 (Wiki Image).
James Madison of Virginia faced the following obstacles, successes, wisdom, and The Federalist Papers concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Madison was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Madison had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Madison was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Madison was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He is known as the “Father of the Constitution” because he played such a key role in its drafting. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Virginia.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Madison helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
- Wrote the Federalist Papers, a series of essays that defended the Constitution and helped to secure its ratification. Madison wrote 29 of the 85 Federalist Papers. The Federalist Papers are considered to be one of the most important works of political theory ever written. They have been studied and debated by scholars and politicians for centuries.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Madison knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Madison understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Madison believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
The Federalist Papers
The Federalist Papers are a series of 85 essays that were written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay under the pseudonym Publius. The essays were published between October 1787 and April 1788 in New York newspapers and were intended to persuade New Yorkers to ratify the Constitution.
The Federalist Papers cover a wide range of topics, including the need for a strong central government, the importance of separation of powers, and the protection of individual rights. The essays are considered to be one of the most important works of political theory ever written and have been studied and debated by scholars and politicians for centuries.
Conclusion
James Madison was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Madison was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He is known as the “Father of the Constitution” because he played such a key role in its drafting. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution, and he wrote 29 of the 85 Federalist Papers, which are considered to be one of the most important works of political theory ever written.
Madison’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Hamilton, Alexander, N.Y., faced obstacles, successes, wisdom, and The Federalist Papers concerning the Constitution.
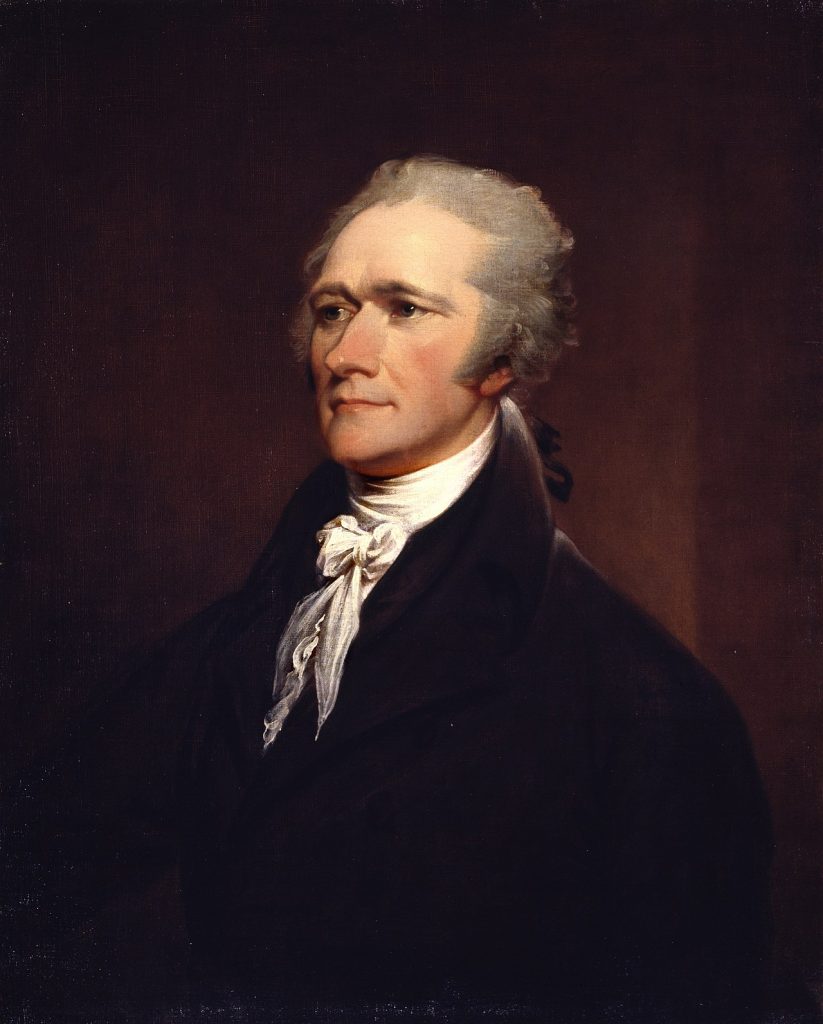

Alexander Hamilton (Wiki Image).
Alexander Hamilton of New York faced the following obstacles, successes, wisdom, and The Federalist Papers concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Hamilton was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Hamilton had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Hamilton was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
- Opposition from anti-federalists who opposed the Constitution altogether. Anti-federalists were concerned that the Constitution gave too much power to the central government and did not adequately protect the rights of individuals and states. Hamilton had to address these concerns in order to secure the ratification of the Constitution.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Hamilton was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause, the Elastic Clause, and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in New York.
- Helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Hamilton helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
- Wrote the Federalist Papers, a series of essays that defended the Constitution and helped to secure its ratification. The Federalist Papers are considered to be one of the most important works of political theory ever written. They have been studied and debated by scholars and politicians for centuries.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Hamilton knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Hamilton understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Hamilton believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
The Federalist Papers
The Federalist Papers are a series of 85 essays that were written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay under the pseudonym Publius. The essays were published between October 1787 and April 1788 in New York newspapers and were intended to persuade New Yorkers to ratify the Constitution.
The Federalist Papers cover a wide range of topics, including the need for a strong central government, the importance of separation of powers, and the protection of individual rights. The essays are considered to be one of the most important works of political theory ever written and have been studied and debated by scholars and politicians for centuries.
Conclusion
Alexander Hamilton was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Hamilton was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also wrote the Federalist Papers, which are considered to be one of the most important works of political theory ever written.
Hamilton’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Morris, Gouverneur, Pa., faced obstacles, successes, wisdom, and wit concerning the Constitution.
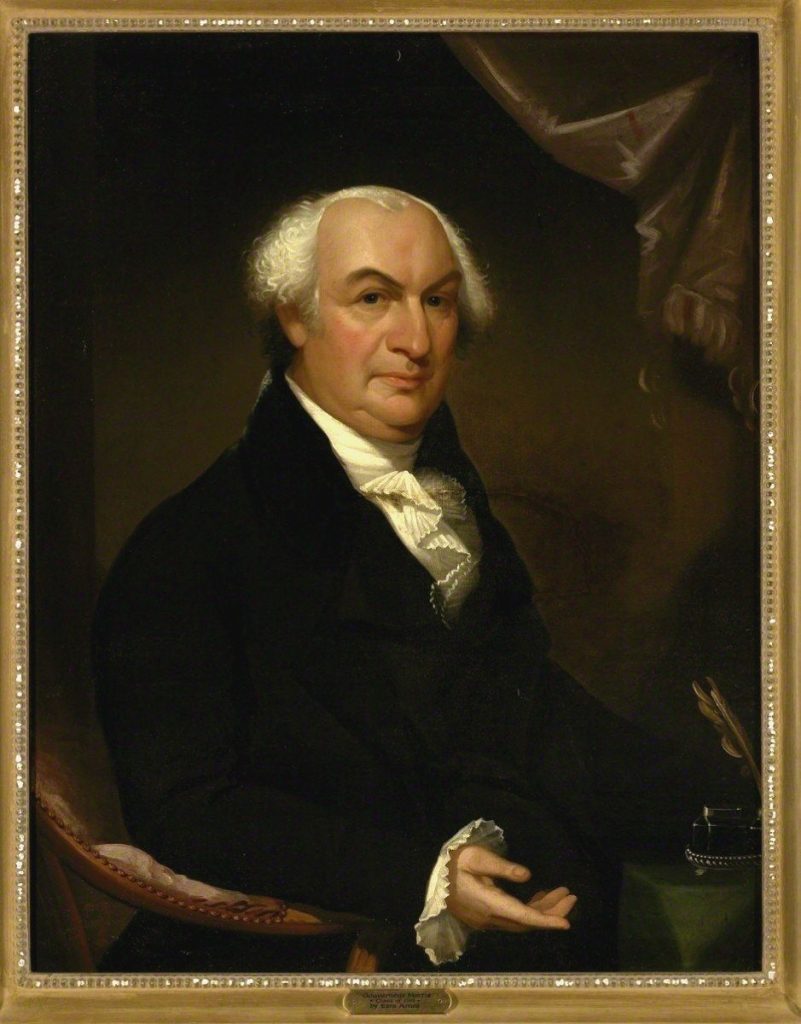

Gouverneur Morris (Wiki Image).
Gouverneur Morris of Pennsylvania faced the following obstacles, successes, wisdom, and wit concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Morris was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Morris had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Morris was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Morris was a respected and influential delegate to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Preamble, the Supremacy Clause, and the Elastic Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Pennsylvania.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Morris helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
- Known for his wit and wisdom. Morris was a brilliant and witty man. He was known for his ability to see both sides of an issue and to find creative solutions to problems. His wit and wisdom were invaluable during the Constitutional Convention.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Morris knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Morris understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Morris believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Wit
Morris was known for his sharp wit and his ability to make others laugh. He often used humor to defuse tensions during the Constitutional Convention. For example, when one delegate proposed that the president should be given the power to declare war, Morris replied: “Then we shall have a perpetual war, for a prince will always be making war if he has the power.”
Morris’s wit and wisdom helped to make him one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. His contributions to the Constitution are significant and enduring.
Conclusion
Gouverneur Morris was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Morris was a man of great wisdom and wit. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced.
Morris’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Morris, Robert, Pa., faced obstacles, successes, wisdom, and financier concerning the Constitution.
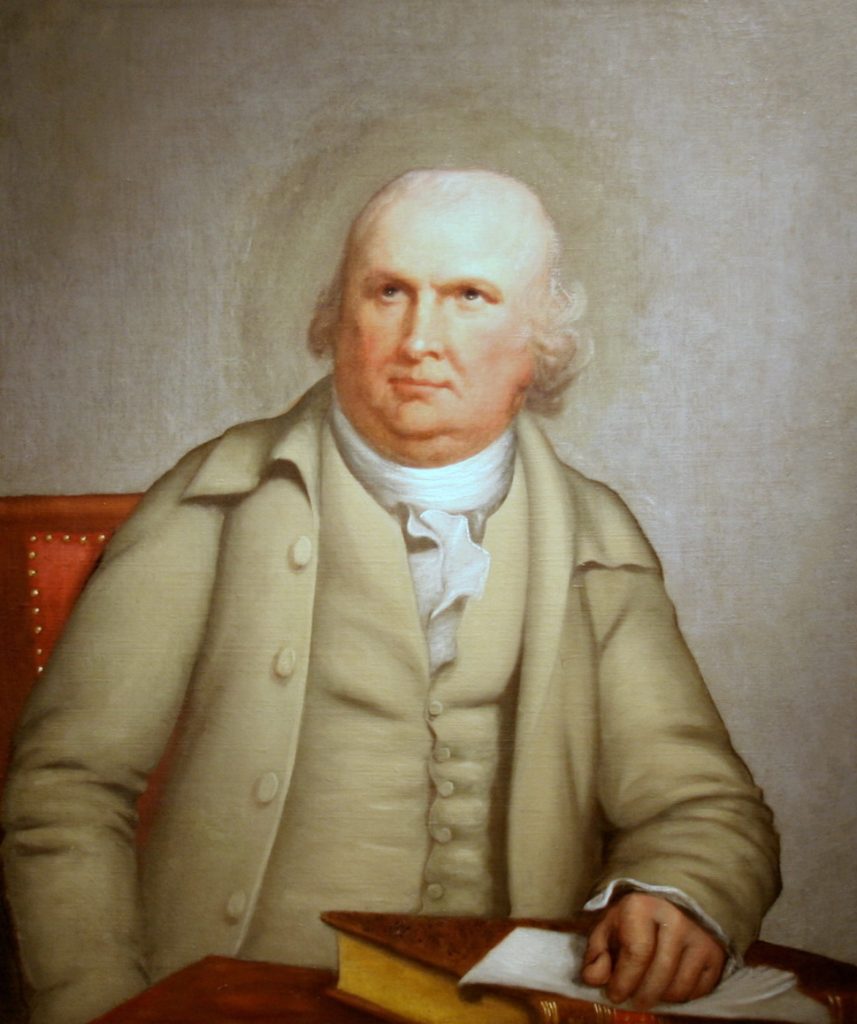

Robert Morris (Wiki Image).
Robert Morris of Pennsylvania faced the following obstacles, successes, wisdom, and financier concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Morris was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Morris had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Morris was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
- Opposition from delegates who did not trust him due to his financial dealings. Morris was a successful financier, but he had also been accused of financial impropriety. He had to overcome these accusations in order to gain the trust of the delegates.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Morris was a respected and influential delegate to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Taxing and Spending Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Pennsylvania.
- Helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Morris helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
- Financed the American Revolution. Morris used his financial skills to finance the American Revolution. He raised money from both domestic and foreign sources, and he also helped to establish the Bank of North America, which provided financial support for the war effort.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Morris knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Morris understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Morris believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Financier
Morris was a successful financier. He made a fortune in shipping and banking. He also served as the Superintendent of Finance for the United States from 1781 to 1784. In this role, he was responsible for managing the country’s finances during the American Revolution.
Morris’s financial skills were essential to the success of the American Revolution. He raised money from both domestic and foreign sources, and he also helped to establish the Bank of North America, which provided financial support for the war effort.
Conclusion
Robert Morris was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Morris was a man of great wisdom and financial expertise. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also financed the American Revolution, which was essential to the country’s success.
Morris’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Wilson, James, PA., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
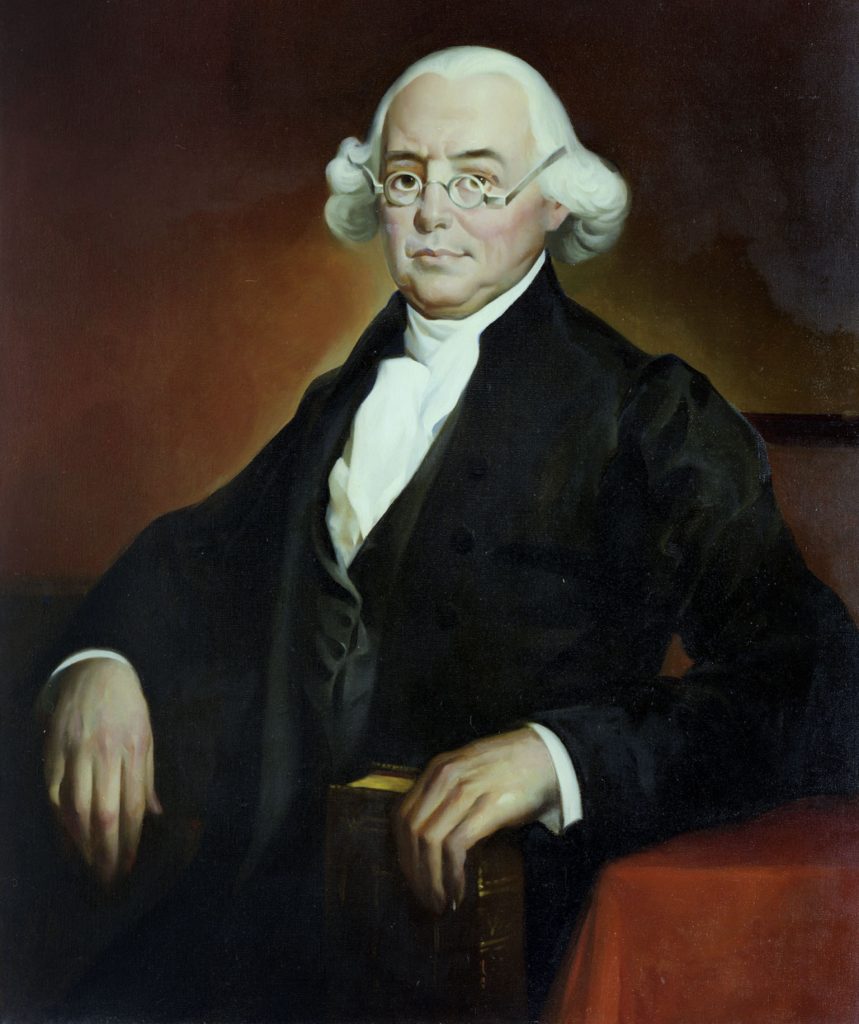

James Wilson (Wiki Image).
James Wilson of Pennsylvania faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Wilson was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Wilson had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Wilson was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Wilson was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Pennsylvania.
- Helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Wilson helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Wilson knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Wilson understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Wilson believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Wilson served as a Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1789 to 1798. He is known for his landmark opinions in cases such as Chisholm v. Georgia, which established the principle of judicial review, and Hylton v. United States, which struck down a federal tax as unconstitutional.
Wilson’s work on the Constitution and his service on the Supreme Court had a profound impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
James Wilson was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Wilson was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as a Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States and wrote landmark opinions that have had a profound impact on the development of the country.
Wilson’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Pinckney, Chas. Cotesworth, S.C., faced obstacles, successes, and ⅗ slavery concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
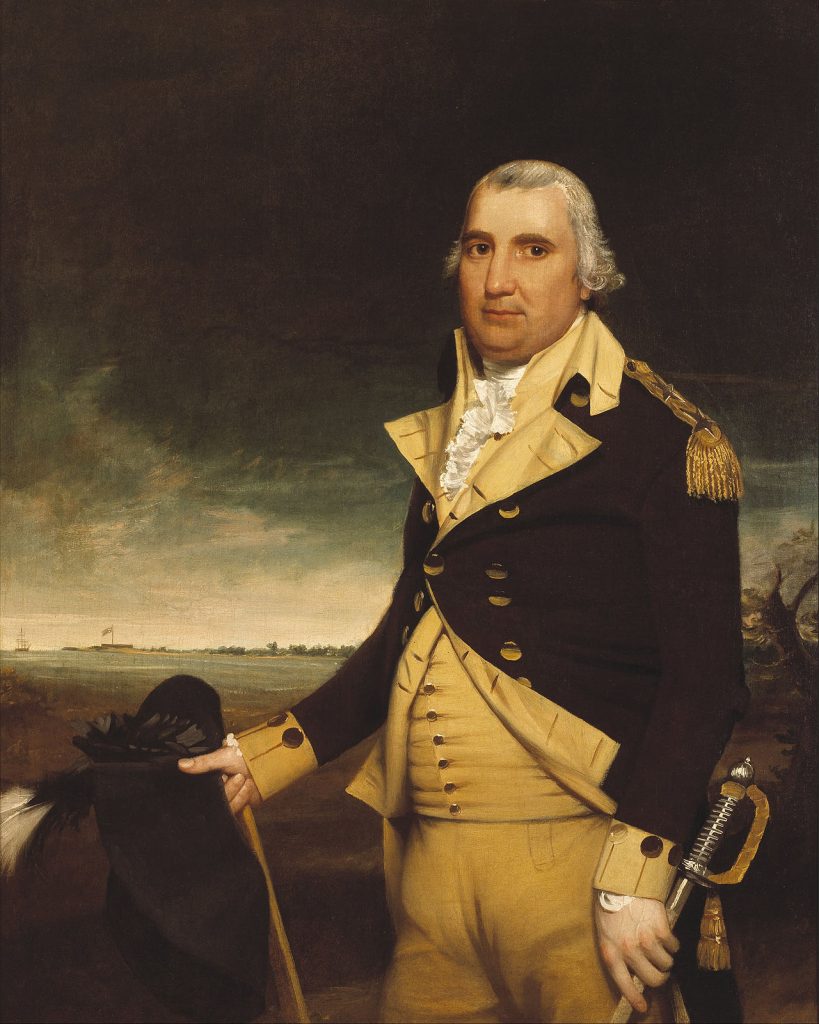

Charles Cotesworth Pinckney (Wiki Image).
Charles Cotesworth Pinckney was a Founding Father of the United States and a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787. He was a strong supporter of a strong central government and was one of the authors of the Three-Fifths Compromise, which counted three-fifths of slaves for the purposes of representation and taxation.
Obstacles
Pinckney faced a number of obstacles in his political career. One obstacle was his support for slavery. Many Northerners opposed slavery, and Pinckney’s support for the Three-Fifths Compromise made him unpopular with some. Additionally, Pinckney was from South Carolina, which was one of the smallest states in the Union. This meant that South Carolina had less political power than other states, and Pinckney had to work harder to get his ideas heard.
Successes
Despite the obstacles he faced, Pinckney had a number of successes in his political career. He was a delegate to the Constitutional Convention and helped to draft the Constitution. He was also elected to the U.S. House of Representatives and served as the governor of South Carolina. Additionally, Pinckney was a successful diplomat and helped to negotiate treaties with France and Spain.
Three-Fifths Compromise
The Three-Fifths Compromise was a compromise between the Northern and Southern states on the issue of slavery. The Northern states wanted to count slaves as people for the purposes of representation, while the Southern states wanted to count slaves as property. The Three-Fifths Compromise counted three-fifths of slaves for the purposes of representation and taxation. This compromise was essential to the creation of the Constitution, as it allowed the Northern and Southern states to reach an agreement on the issue of slavery.
Leadership
Pinckney was a leader in both the government and the military. He served as the governor of South Carolina and as a delegate to the Constitutional Convention. He also served in the Continental Army during the American Revolution and was wounded in the Battle of Brandywine.
Conclusion
Charles Cotesworth Pinckney was a Founding Father of the United States who faced a number of obstacles but had a number of successes in his political career. He was a strong supporter of a strong central government and was one of the authors of the Three-Fifths Compromise. He was also a leader in both the government and the military.
It is important to note that Pinckney’s support for slavery is a complex and controversial issue. Some people believe that he should be condemned for his support of slavery, while others believe that he was a product of his time and that his support for slavery should not overshadow his other accomplishments.
A.I. Pinckney, Chas., S.C., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
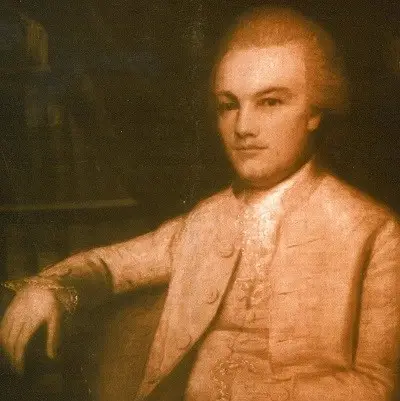

Charles Pinckney (Wiki Image).
Charles Pinckney of South Carolina faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles:
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Pinckney was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Pinckney had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Pinckney was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes:
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Pinckney was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in South Carolina.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Pinckney helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
Wisdom:
- Understood the importance of compromise. Pinckney knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Pinckney understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Pinckney believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Pinckney served as the Governor of South Carolina from 1796 to 1798 and again from 1806 to 1808. He also served as the Minister to France from 1799 to 1801.
Pinckney’s work on the Constitution and his service as Governor of South Carolina and Minister to France had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
Charles Pinckney was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Pinckney was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as the Governor of South Carolina, and Minister to France, and his work in these positions had a significant impact on the development of the country.
Pinckney’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Rutledge, John, S.C., faced obstacles, successes, and ⅗ slavery concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
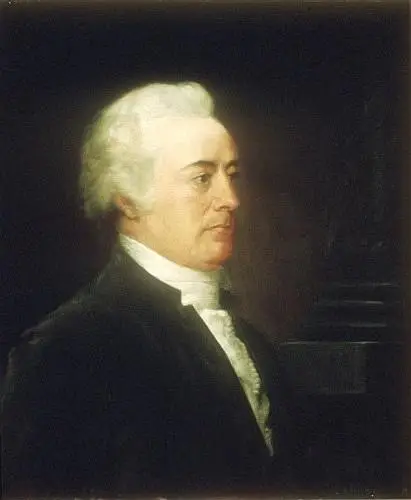

John Rutledge (Wiki Image).
John Rutledge of South Carolina faced the following obstacles, successes, and 3/5 slavery concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles:
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Rutledge was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Rutledge had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Rutledge was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes:
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Rutledge was a respected and influential delegate to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Commerce Clause, which gave Congress the power to regulate interstate commerce. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in South Carolina.
- Helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Rutledge helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
3/5 slavery
The 3/5 Compromise was a compromise reached at the Constitutional Convention that counted three-fifths of each state’s slave population for the purpose of determining the state’s total population for legislative representation and taxation. This compromise gave slave states more representatives and more presidential electoral votes than if slaves had not been counted.
Rutledge supported the 3/5 Compromise as a necessary compromise in order to secure the ratification of the Constitution. However, he also believed that slavery was morally wrong and that it should eventually be abolished.
Led the government in the past and future
Rutledge served as the first Chief Justice of the United States Supreme Court from 1789 to 1791. He also served as the Governor of South Carolina on two occasions.
Rutledge’s work on the Constitution and his service as Chief Justice of the Supreme Court had a profound impact on the development of the United States government. He helped to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Conclusion
John Rutledge was a complex and controversial figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his controversies, Rutledge was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring.
Additional thoughts
It is important to note that the 3/5 Compromise was a flawed compromise. It gave slave states more power in the federal government, even though slaves were not considered citizens and had no legal rights. The 3/5 Compromise contributed to the growing sectional tensions that eventually led to the Civil War.
However, it is also important to remember that the Founding Fathers were trying to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states, including the slave states. They knew that they could not abolish slavery immediately, but they hoped that the Constitution would eventually lead to the abolition of slavery.
The 13th Amendment to the Constitution, which abolished slavery, was ratified in 1865. This was a major victory for the forces of freedom and justice.
The legacy of John Rutledge is a complex one. He was a Founding Father who played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. He was also a slave owner. His work on the Constitution had a profound impact on the development of the United States government, but his ownership of slaves is a dark stain on his legacy.
It is up to each individual to decide how they view John Rutledge. He was a complex and flawed figure, but he was also a Founding Father who played a key role in shaping the United States government. His contributions to the Constitution are significant and enduring.
A.I. Butler, Pierce, S.C., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
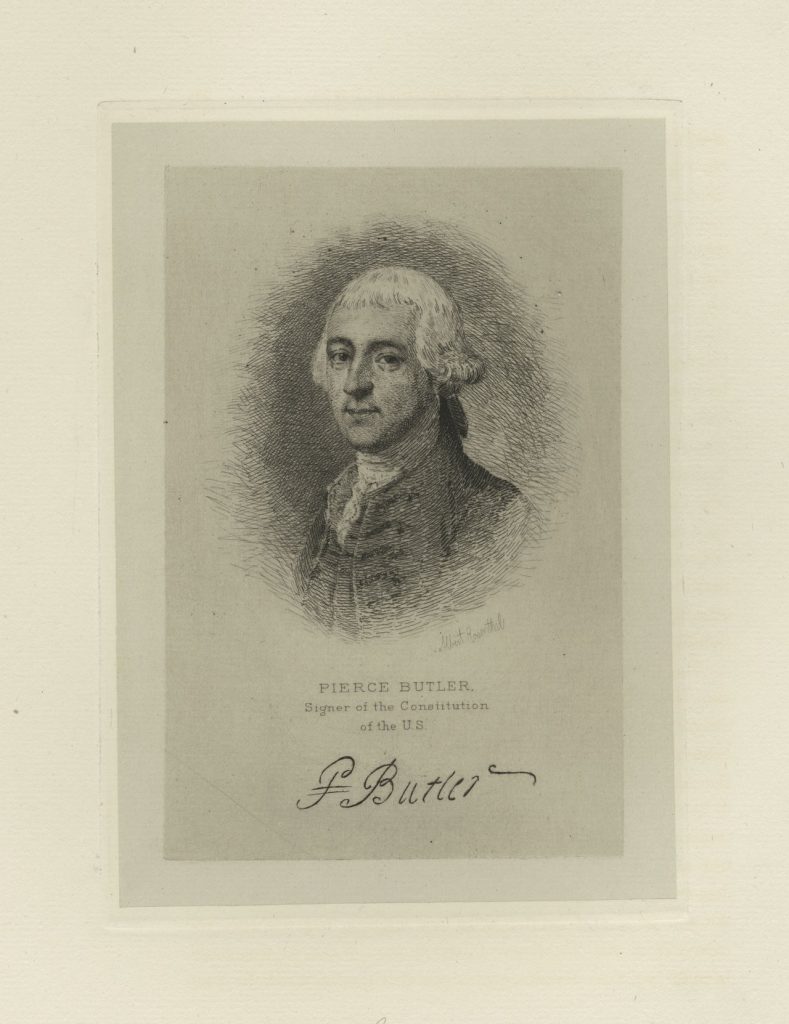

Pierce Butler (Wiki Image).
Pierce Butler of South Carolina faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Butler was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Butler had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Butler was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Butler was an influential delegate to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Fugitive Slave Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in South Carolina.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Butler helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Butler knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Butler understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Butler believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Butler served as a United States Senator from South Carolina from 1789 to 1796 and again from 1803 to 1804. He also served as a Justice of the South Carolina Supreme Court from 1797 to 1803.
Butler’s work on the Constitution and his service as a United States Senator and Justice of the South Carolina Supreme Court had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
Pierce Butler was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Butler was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as a United States Senator and Justice of the South Carolina Supreme Court, and his work in these positions had a significant impact on the development of the country.
Butler’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Sherman, Roger, Conn., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
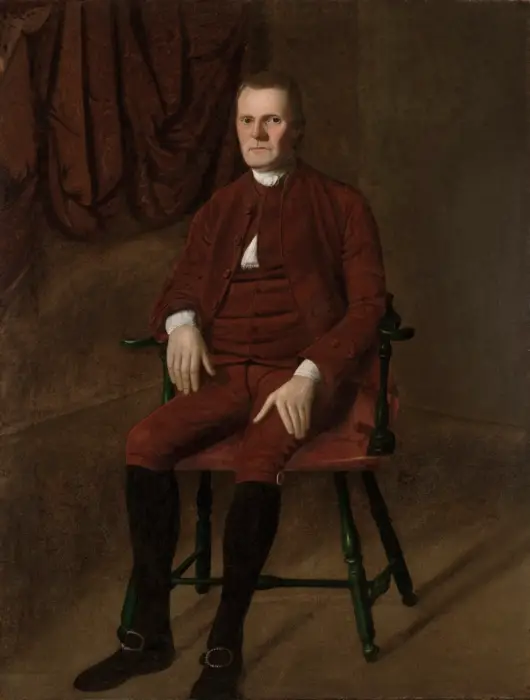

Roger Sherman (Wiki Image).
Roger Sherman of Connecticut faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Sherman was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Sherman had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Sherman was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Sherman was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Commerce Clause and the Taxing and Spending Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Connecticut.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Sherman helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Sherman knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Sherman understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Sherman believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Sherman served as a member of the Continental Congress from 1774 to 1783. He also served as a United States Senator from Connecticut from 1789 to 1793 and again from 1795 to 1796. He also served as the Mayor of New Haven, Connecticut from 1784 to 1791.
Sherman’s work on the Constitution and his service as a member of the Continental Congress, United States Senator, and Mayor of New Haven had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
Roger Sherman was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Sherman was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as a member of the Continental Congress, United States Senator, and Mayor of New Haven, and his work in these positions had a significant impact on the development of the country.
Sherman’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Johnson, William Samuel, Conn., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
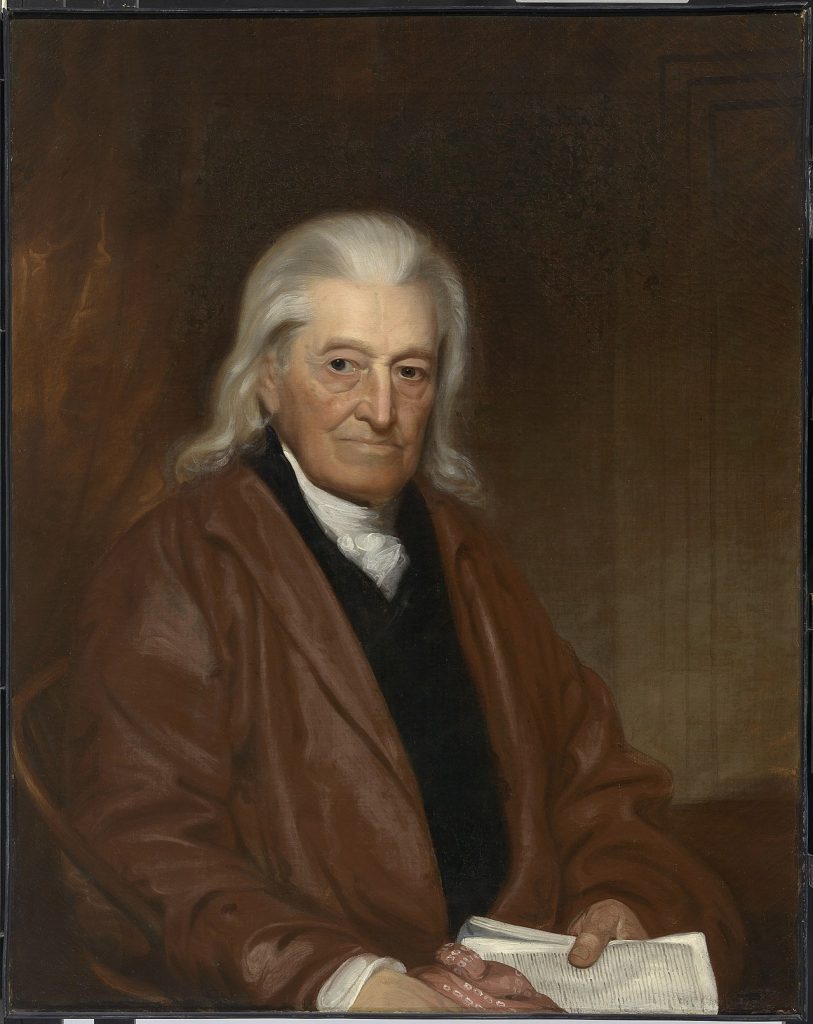

William Samuel Johnson (Wiki Image).
William Samuel Johnson of Connecticut faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Johnson was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Johnson had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Johnson was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Johnson was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Connecticut.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Johnson helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Johnson knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Johnson understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Johnson believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Johnson served as a United States Senator from Connecticut from 1789 to 1791. He also served as the president of Columbia College (now Columbia University) from 1787 to 1800.
Johnson’s work on the Constitution and his service as a United States Senator and president of Columbia College had a significant impact on the development of the United States government and education. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
William Samuel Johnson was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Johnson was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government and education are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as a United States Senator and president of Columbia College, and his work in these positions had a significant impact on the development of the country.
Johnson’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. McHenry, James, Md., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
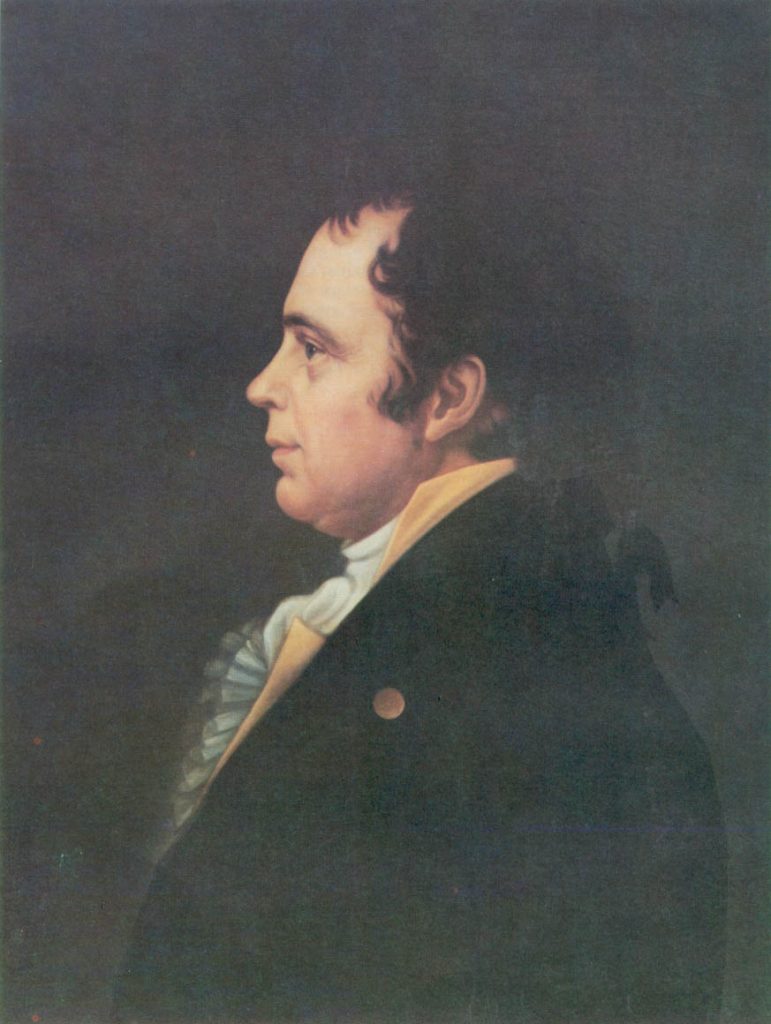

James McHenry (Wiki Image).
James McHenry of Maryland faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. McHenry was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. McHenry had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. McHenry was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. McHenry was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Maryland.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that McHenry helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. McHenry knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. McHenry understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. McHenry believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
McHenry served as the third United States Secretary of War from 1796 to 1800. He was responsible for overseeing the development of the United States Army and Navy. He also played a key role in the response to the XYZ Affair, a diplomatic crisis with France in 1797.
McHenry’s work on the Constitution and his service as Secretary of War had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
James McHenry was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, McHenry was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as Secretary of War and played a key role in the development of the United States Army and Navy.
McHenry’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Read, George, Del., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
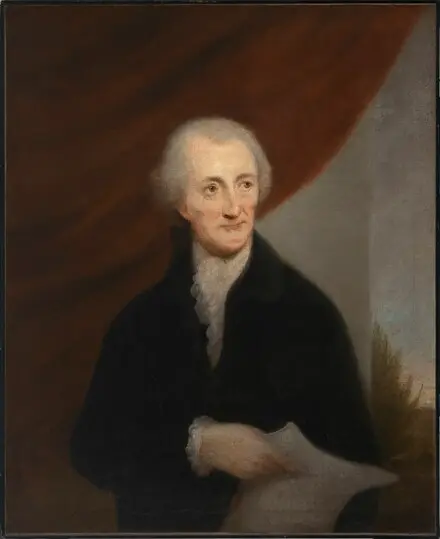

George Read (Wiki Image).
George Read of Delaware faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Read was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Read had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Read was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Read was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Judicial Branch. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Delaware.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Read helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
- Served as a United States Senator from Delaware. Read served as a United States Senator from Delaware from 1789 to 1795. He was a strong advocate for the Constitution and for the principles of federalism.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Read knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Read understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Read believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Read served as a United States Senator from Delaware from 1789 to 1795. He was a strong advocate for the Constitution and for the principles of federalism.
Read’s work on the Constitution and his service as a United States Senator had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
George Read was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Read was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as a United States Senator and was a strong advocate for the Constitution and the principles of federalism.
Read’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
In addition to his accomplishments as a Founding Father and United States Senator, Read also served as the Chief Justice of the Delaware Supreme Court from 1795 until his death in 1800. He was a respected jurist and a strong advocate for the rule of law.
Read is remembered as a man of great wisdom, integrity, and compassion. He was a dedicated public servant who made significant contributions to the development of the United States government.
A.I. Bassett, Richard, Del., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Richard Bassett (Wiki Image).
Richard Bassett of Delaware faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Bassett was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Bassett had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Bassett was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Led the fight for ratification of the Constitution in Delaware. Delaware was the first state to ratify the Constitution, and Bassett was one of the leading figures in the ratification campaign. He gave a number of speeches and wrote articles in support of the Constitution, and he worked tirelessly to persuade his fellow Delawareans to vote for ratification.
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Bassett was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Delaware.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Bassett helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Bassett knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Bassett understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Bassett believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Bassett served as the Governor of Delaware from 1799 to 1801. He was a popular and effective governor, and he is considered to be one of the most important figures in Delaware history.
Bassett’s work on the Constitution and his service as Governor of Delaware had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
Richard Bassett was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Bassett was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He led the fight for ratification of the Constitution in Delaware, helped draft several important provisions of the Constitution, and played a key role in creating a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as Governor of Delaware and was a popular and effective leader.
Bassett’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Spaight, Richard Dobbs, N.C., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Richard Spaight (Wiki Image).
Richard Dobbs Spaight of North Carolina faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Spaight was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Spaight had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Spaight was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Spaight was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in North Carolina.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Spaight helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
- Served as the Governor of North Carolina from 1792 to 1795. Spaight was a popular and effective governor, and he is considered to be one of the most important figures in North Carolina history.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Spaight knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Spaight understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Spaight believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Spaight served as the Governor of North Carolina from 1792 to 1795. He was a popular and effective governor, and he is considered to be one of the most important figures in North Carolina history.
Spaight’s work on the Constitution and his service as Governor of North Carolina had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
Richard Dobbs Spaight was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Spaight was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced and served as the popular and effective Governor of North Carolina.
Spaight’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Blount, William, N.C., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

William Blount (Wiki Image).
William Blount of North Carolina faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Blount was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Blount had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Blount was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Blount was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in North Carolina.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Blount helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
- Served as the Governor of the Southwest Territory from 1790 to 1796. Blount was the first governor of the Southwest Territory, which was later divided into the states of Tennessee, Kentucky, Alabama, and Mississippi. He played a key role in the development of the territory and in its eventual admission to the Union as the state of Tennessee.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Blount knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Blount understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Blount believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Blount served as the Governor of the Southwest Territory from 1790 to 1796. He also served as one of the first two United States Senators from Tennessee from 1796 to 1797.
Blount’s work on the Constitution and his service as Governor of the Southwest Territory and United States Senator had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
William Blount was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Blount was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced, served as the Governor of the Southwest Territory and one of the first two United States Senators from Tennessee, and was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Blount’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I Williamson, Hugh, N.C., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Hugh Williamson (Wiki Image).
Hugh Williamson, a delegate from North Carolina to the Constitutional Convention, was a complex and fascinating figure. He faced obstacles, achieved successes, and demonstrated wisdom concerning the Constitution. He also led the government in both the past and future.
Obstacles
One of the biggest obstacles that Williamson faced was his own state’s reluctance to ratify the Constitution. North Carolina was initially one of two states that refused to do so, and Williamson played a key role in changing the public’s mind. He wrote essays and gave speeches in support of the Constitution, and he even attended the second North Carolina ratification convention as a delegate. Ultimately, North Carolina became the 12th state to ratify the Constitution in 1789.
Another obstacle that Williamson faced was his own health. He suffered from chronic asthma throughout his life, and it often made it difficult for him to participate in public life. However, Williamson was determined to serve his country, and he overcame his health challenges to make significant contributions to the government.
Successes
Williamson’s greatest success was his role in helping to draft and ratify the Constitution. He was a leading voice in the convention, and he played a key role in shaping the document’s final form. Williamson was also a strong advocate for the Constitution in North Carolina, and his efforts helped to ensure that the state eventually ratified it.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Williamson also had a successful career in government. He served in the North Carolina House of Commons, the Continental Congress, and the United States House of Representatives. Williamson was also a member of the Electoral College in 1789 and 1793.
Wisdom
Williamson was a wise and thoughtful man, and his insights into the Constitution are still relevant today. He understood the importance of balance between the federal government and the states, and he believed that the Constitution was the best way to ensure that the United States would remain a free and prosperous nation.
Williamson was also a strong advocate for education and economic development. He believed that the government should play a role in promoting these important goals. Williamson’s wisdom and foresight can be seen in his many contributions to the government, as well as in his writings on a variety of topics.
Leading the Government in the Past and Future
Williamson’s leadership in the government can be seen in both the past and future. He was a key figure in drafting and ratifying the Constitution, and he also served in a number of important government positions. Williamson’s insights into the Constitution and his commitment to education and economic development continue to be relevant today.
In the past, Williamson’s leadership helped to shape the United States into a free and prosperous nation. In the future, his wisdom can continue to guide us as we work to build a better future for all Americans.
Here are some specific examples of Williamson’s leadership in the government:
- At the Constitutional Convention, Williamson proposed the Connecticut Compromise, which helped to resolve the impasse between large and small states over representation in the new government.
- Williamson was also a strong advocate for the inclusion of a Bill of Rights in the Constitution. He believed that it was important to protect individual liberties from government overreach.
- In the North Carolina House of Commons, Williamson played a key role in passing legislation that established public schools and supported economic development.
- In the Continental Congress, Williamson served on a number of important committees, including the Committee on Foreign Affairs and the Committee on Finance.
- In the United States House of Representatives, Williamson was a member of the Ways and Means Committee and the Committee on Commerce and Manufactures.
Williamson’s leadership in the government helped to shape the United States into the nation it is today. He was a strong advocate for individual liberty, limited government, and economic development. His wisdom and foresight continue to be relevant today, and his legacy continues to inspire us.
A.I. Jenifer, Daniel of St. Thomas, Md., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Daniel of St. Thomas Jenifer (Wiki Image).
Daniel of St. Thomas Jenifer, a delegate from Maryland to the Constitutional Convention, faced a number of obstacles, achieved successes, and demonstrated wisdom concerning the Constitution. He also led the government in both the past and future.
Obstacles
One of the biggest obstacles that Jenifer faced was his own health. He suffered from gout and other ailments throughout his life, and they often made it difficult for him to participate in public life. However, Jenifer was determined to serve his country, and he overcame his health challenges to make significant contributions to the government.
Another obstacle that Jenifer faced was the opposition of some Marylanders to the Constitution. Maryland was initially one of two states that refused to ratify the document, and Jenifer played a key role in changing the public’s mind. He wrote essays and gave speeches in support of the Constitution, and he even attended the second Maryland ratification convention as a delegate. Ultimately, Maryland became the 12th state to ratify the Constitution in 1789.
Successes
Jenifer’s greatest success was his role in helping to draft and ratify the Constitution. He was a leading voice in the convention, and he played a key role in shaping the document’s final form. Jenifer was also a strong advocate for the Constitution in Maryland, and his efforts helped to ensure that the state eventually ratified it.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Jenifer also had a successful career in government. He served in the Maryland House of Delegates, the Maryland Senate, the Continental Congress, and the United States House of Representatives. Jenifer was also the president of the Maryland Senate from 1777 to 1780.
Wisdom
Jenifer was a wise and thoughtful man, and his insights into the Constitution are still relevant today. He understood the importance of balance between the federal government and the states, and he believed that the Constitution was the best way to ensure that the United States would remain a free and prosperous nation.
Jenifer was also a strong advocate for individual liberty and the rule of law. He believed that the government should be limited in its power and that the rights of the people should be protected. Jenifer’s wisdom and foresight can be seen in his many contributions to the government, as well as in his writings on a variety of topics.
Leading the Government in the Past and Future
Jenifer’s leadership in the government can be seen in both the past and future. He was a key figure in drafting and ratifying the Constitution, and he also served in a number of important government positions. Jenifer’s insights into the Constitution and his commitment to individual liberty, limited government, and the rule of law continue to be relevant today.
In the past, Jenifer’s leadership helped to shape the United States into a free and prosperous nation. In the future, his wisdom can continue to guide us as we work to build a better future for all Americans.
Here are some specific examples of Jenifer’s leadership in the government:
- At the Constitutional Convention, Jenifer proposed a number of important amendments to the Constitution, including the amendment that guarantees the right to a speedy and public trial by an impartial jury.
- Jenifer was also a strong advocate for the inclusion of a Bill of Rights in the Constitution. He believed that it was important to protect individual liberties from government overreach.
- In the Continental Congress, Jenifer served on a number of important committees, including the Committee on Foreign Affairs and the Committee of the Whole.
- In the United States House of Representatives, Jenifer was a member of the Committee on Ways and Means and the Committee on Commerce and Manufactures.
Jenifer’s leadership in the government helped to shape the United States into the nation it is today. He was a strong advocate for individual liberty, limited government, and the rule of law. His wisdom and foresight continue to be relevant today, and his legacy continues to inspire us.
A.I. King, Rufus, Mass., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Rufus King (Wiki Image).
Rufus King, a delegate from Massachusetts to the Constitutional Convention, faced a number of obstacles, achieved successes, and demonstrated wisdom concerning the Constitution. He also led the government in both the past and future.
Obstacles
One of the biggest obstacles that King faced was the opposition of some Massachusetts residents to the Constitution. Massachusetts was initially one of two states that refused to ratify the document, and King played a key role in changing the public’s mind. He wrote essays and gave speeches in support of the Constitution, and he even attended the second Massachusetts ratification convention as a delegate. Ultimately, Massachusetts became the sixth state to ratify the Constitution in 1788.
Another obstacle that King faced was his own health. He suffered from asthma and other ailments throughout his life, and they often made it difficult for him to participate in public life. However, King was determined to serve his country, and he overcame his health challenges to make significant contributions to the government.
Successes
King’s greatest success was his role in helping to draft and ratify the Constitution. He was a leading voice in the convention, and he played a key role in shaping the document’s final form. King was also a strong advocate for the Constitution in Massachusetts, and his efforts helped to ensure that the state eventually ratified it.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, King also had a successful career in government. He served in the Massachusetts Senate, the Continental Congress, the United States Senate, and the United States House of Representatives. King was also the United States Minister to Great Britain from 1796 to 1803 and again from 1825 to 1826.
Wisdom
King was a wise and thoughtful man, and his insights into the Constitution are still relevant today. He understood the importance of balance between the federal government and the states, and he believed that the Constitution was the best way to ensure that the United States would remain a free and prosperous nation.
King was also a strong advocate for individual liberty and the rule of law. He believed that the government should be limited in its power and that the rights of the people should be protected. King’s wisdom and foresight can be seen in his many contributions to the government, as well as in his writings on a variety of topics.
Leading the Government in the Past and Future
King’s leadership in the government can be seen in both the past and future. He was a key figure in drafting and ratifying the Constitution, and he also served in a number of important government positions. King’s insights into the Constitution and his commitment to individual liberty, limited government, and the rule of law continue to be relevant today.
In the past, King’s leadership helped to shape the United States into a free and prosperous nation. In the future, his wisdom can continue to guide us as we work to build a better future for all Americans.
Here are some specific examples of King’s leadership in the government:
- At the Constitutional Convention, King proposed a number of important amendments to the Constitution, including the amendment that guarantees the right to a trial by jury in civil cases.
- King was also a strong advocate for the inclusion of a Bill of Rights in the Constitution. He believed that it was important to protect individual liberties from government overreach.
- In the United States Senate, King served on a number of important committees, including the Committee on Foreign Relations and the Committee on Finance.
- As the United States Minister to Great Britain, King played a key role in negotiating the Jay Treaty, which helped to improve relations between the two countries.
King’s leadership in the government helped to shape the United States into the nation it is today. He was a strong advocate for individual liberty, limited government, and the rule of law. His wisdom and foresight continue to be relevant today, and his legacy continues to inspire us.
A.I. Gorham, Nathaniel, Mass., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
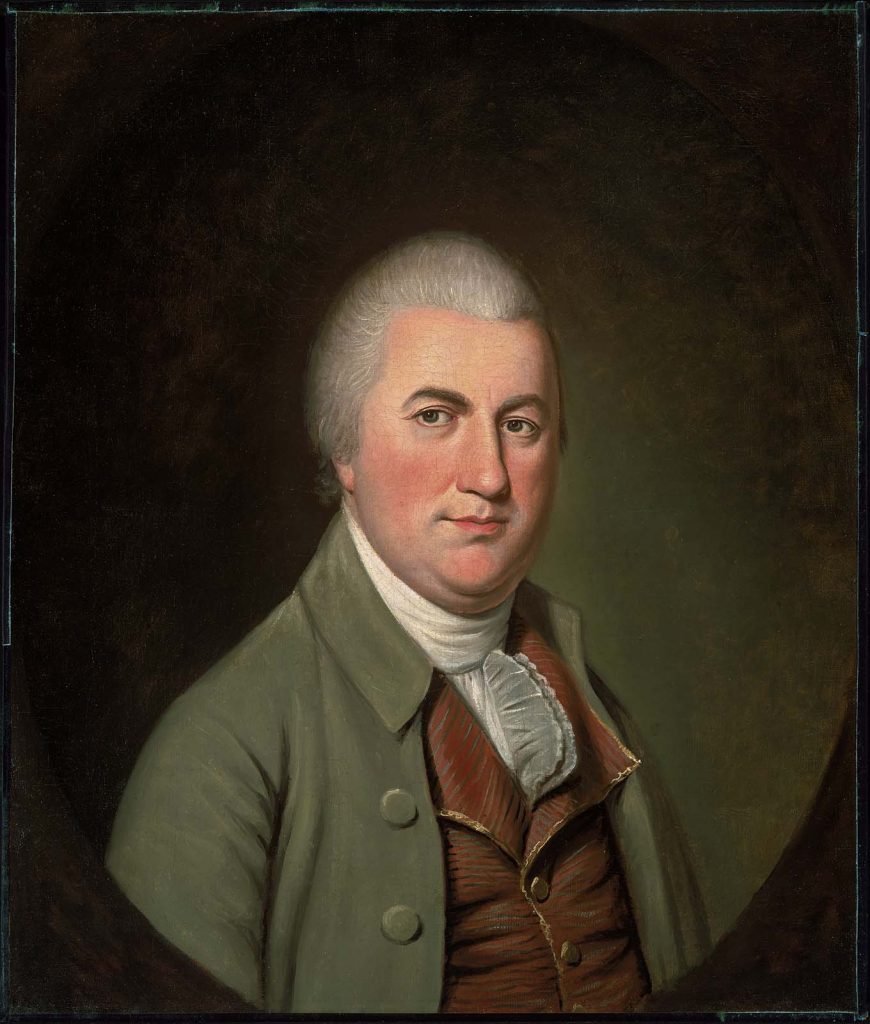

Nathaniel Gorham (Wiki Image).
Nathaniel Gorham, a delegate from Massachusetts to the Constitutional Convention, faced a number of obstacles, achieved successes, and demonstrated wisdom concerning the Constitution. He also led the government in both the past and future.
Obstacles
One of the biggest obstacles that Gorham faced was his own health. He suffered from gout and other ailments throughout his life, and they often made it difficult for him to participate in public life. However, Gorham was determined to serve his country, and he overcame his health challenges to make significant contributions to the government.
Another obstacle that Gorham faced was the opposition of some Massachusetts residents to the Constitution. Massachusetts was initially one of two states that refused to ratify the document, and Gorham played a key role in changing the public’s mind. He wrote essays and gave speeches in support of the Constitution, and he even attended the second Massachusetts ratification convention as a delegate. Ultimately, Massachusetts became the sixth state to ratify the Constitution in 1788.
Successes
Gorham’s greatest success was his role in helping to draft and ratify the Constitution. He was a leading voice in the convention, and he played a key role in shaping the document’s final form. Gorham was also a strong advocate for the Constitution in Massachusetts, and his efforts helped to ensure that the state eventually ratified it.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Gorham also had a successful career in government. He served in the Massachusetts House of Representatives, the Massachusetts Senate, the Continental Congress, and the United States Senate. Gorham was also the President of the Continental Congress from 1786 to 1787.
Wisdom
Gorham was a wise and thoughtful man, and his insights into the Constitution are still relevant today. He understood the importance of balance between the federal government and the states, and he believed that the Constitution was the best way to ensure that the United States would remain a free and prosperous nation.
Gorham was also a strong advocate for individual liberty and the rule of law. He believed that the government should be limited in its power and that the rights of the people should be protected. Gorham’s wisdom and foresight can be seen in his many contributions to the government, as well as in his writings on a variety of topics.
Leading the Government in the Past and Future
Gorham’s leadership in the government can be seen in both the past and future. He was a key figure in drafting and ratifying the Constitution, and he also served in a number of important government positions. Gorham’s insights into the Constitution and his commitment to individual liberty, limited government, and the rule of law continue to be relevant today.
In the past, Gorham’s leadership helped to shape the United States into a free and prosperous nation. In the future, his wisdom can continue to guide us as we work to build a better future for all Americans.
Here are some specific examples of Gorham’s leadership in the government:
- At the Constitutional Convention, Gorham chaired the Committee of the Whole, which was responsible for debating and amending the Constitution. He also served on the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the initial language of the Constitution.
- Gorham was a strong advocate for the inclusion of a Bill of Rights in the Constitution. He believed that it was important to protect individual liberties from government overreach.
- In the United States Senate, Gorham served on a number of important committees, including the Committee on Foreign Relations and the Committee on Finance.
- As the President of the Continental Congress, Gorham played a key role in negotiating the Treaty of Paris, which ended the American Revolutionary War.
Gorham’s leadership in the government helped to shape the United States into the nation it is today. He was a strong advocate for individual liberty, limited government, and the rule of law. His wisdom and foresight continue to be relevant today, and his legacy continues to inspire us.
A.I. Dayton, Jonathan, N.J., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Jonathan Dayton (Wiki Image).
Jonathan Dayton, a delegate from New Jersey to the Constitutional Convention, faced a number of obstacles, achieved successes, and demonstrated wisdom concerning the Constitution. He also led the government in both the past and future.
Obstacles
One of the biggest obstacles that Dayton faced was the opposition of some New Jersey residents to the Constitution. New Jersey was initially one of two states that refused to ratify the document, and Dayton played a key role in changing the public’s mind. He wrote essays and gave speeches in support of the Constitution, and he even attended the second New Jersey ratification convention as a delegate. Ultimately, New Jersey became the 12th state to ratify the Constitution in 1789.
Another obstacle that Dayton faced was his own health. He suffered from asthma and other ailments throughout his life, and they often made it difficult for him to participate in public life. However, Dayton was determined to serve his country, and he overcame his health challenges to make significant contributions to the government.
Successes
Dayton’s greatest success was his role in helping to draft and ratify the Constitution. He was a leading voice in the convention, and he played a key role in shaping the document’s final form. Dayton was also a strong advocate for the Constitution in New Jersey, and his efforts helped to ensure that the state eventually ratified it.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Dayton also had a successful career in government. He served in the New Jersey House of Assembly, the New Jersey Senate, the United States House of Representatives, and the United States Senate. Dayton was also the Speaker of the New Jersey House of Assembly from 1780 to 1782 and again from 1784 to 1785.
Wisdom
Dayton was a wise and thoughtful man, and his insights into the Constitution are still relevant today. He understood the importance of balance between the federal government and the states, and he believed that the Constitution was the best way to ensure that the United States would remain a free and prosperous nation.
Dayton was also a strong advocate for individual liberty and the rule of law. He believed that the government should be limited in its power and that the rights of the people should be protected. Dayton’s wisdom and foresight can be seen in his many contributions to the government, as well as in his writings on a variety of topics.
Leading the Government in the Past and Future
Dayton’s leadership in the government can be seen in both the past and future. He was a key figure in drafting and ratifying the Constitution, and he also served in a number of important government positions. Dayton’s insights into the Constitution and his commitment to individual liberty, limited government, and the rule of law continue to be relevant today.
In the past, Dayton’s leadership helped to shape the United States into a free and prosperous nation. In the future, his wisdom can continue to guide us as we work to build a better future for all Americans.
Here are some specific examples of Dayton’s leadership in the government:
- At the Constitutional Convention, Dayton was a member of the Committee on Style and Arrangement, which was responsible for drafting the final language of the Constitution. He also served on the Committee of the Whole, which was responsible for debating and amending the Constitution.
- Dayton was a strong advocate for the inclusion of a Bill of Rights in the Constitution. He believed that it was important to protect individual liberties from government overreach.
- In the United States House of Representatives, Dayton served on a number of important committees, including the Committee on Foreign Affairs and the Committee on Ways and Means.
- As the Speaker of the New Jersey House of Assembly, Dayton played a key role in passing legislation that supported the American Revolutionary War and established the New Jersey Constitution.
Dayton’s leadership in the government helped to shape the United States into the nation it is today. He was a strong advocate for individual liberty, limited government, and the rule of law. His wisdom and foresight continue to be relevant today, and his legacy continues to inspire us.
A.I. Carroll, Daniel, Md., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
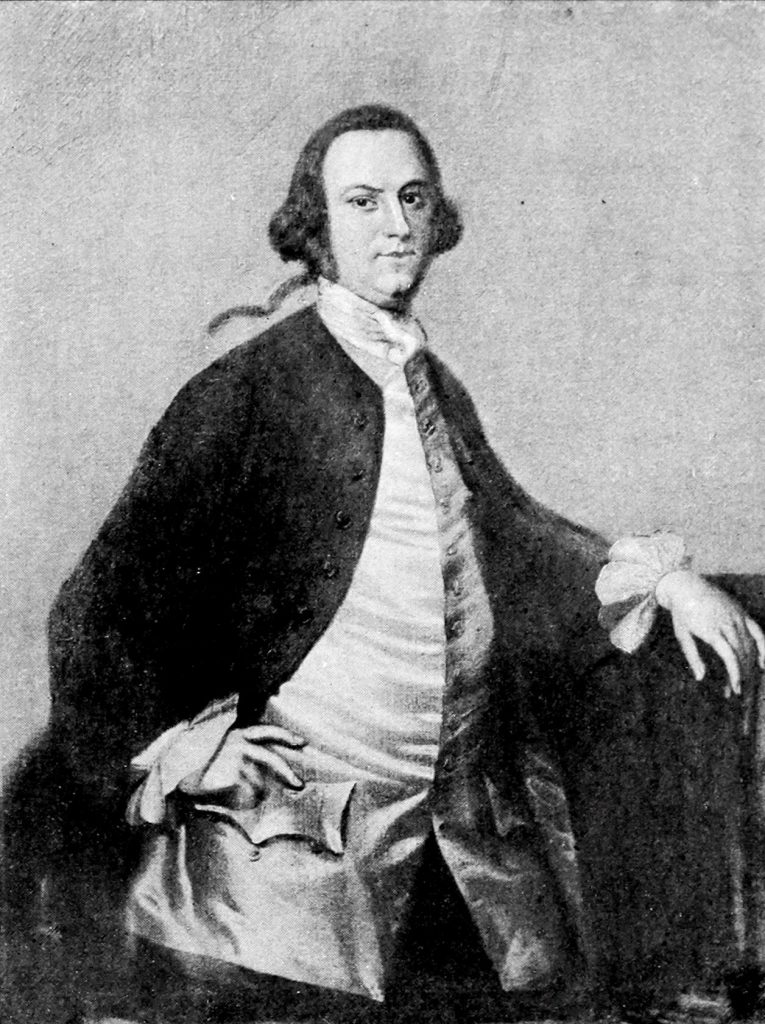

Daniel Carroll (Wiki Image).
Daniel Carroll of Maryland faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Carroll was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Carroll had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Carroll was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Carroll was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Maryland.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Carroll helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Carroll knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Carroll understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Carroll believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Carroll served as a United States Representative from Maryland from 1789 to 1793. He also served as a United States Senator from Maryland from 1796 to 1800.
Carroll’s work on the Constitution and his service as a United States Representative and Senator had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
Daniel Carroll was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Carroll was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as a United States Representative and Senator, and his work in these positions had a significant impact on the development of the country.
Carroll’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Few, William, Ga., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
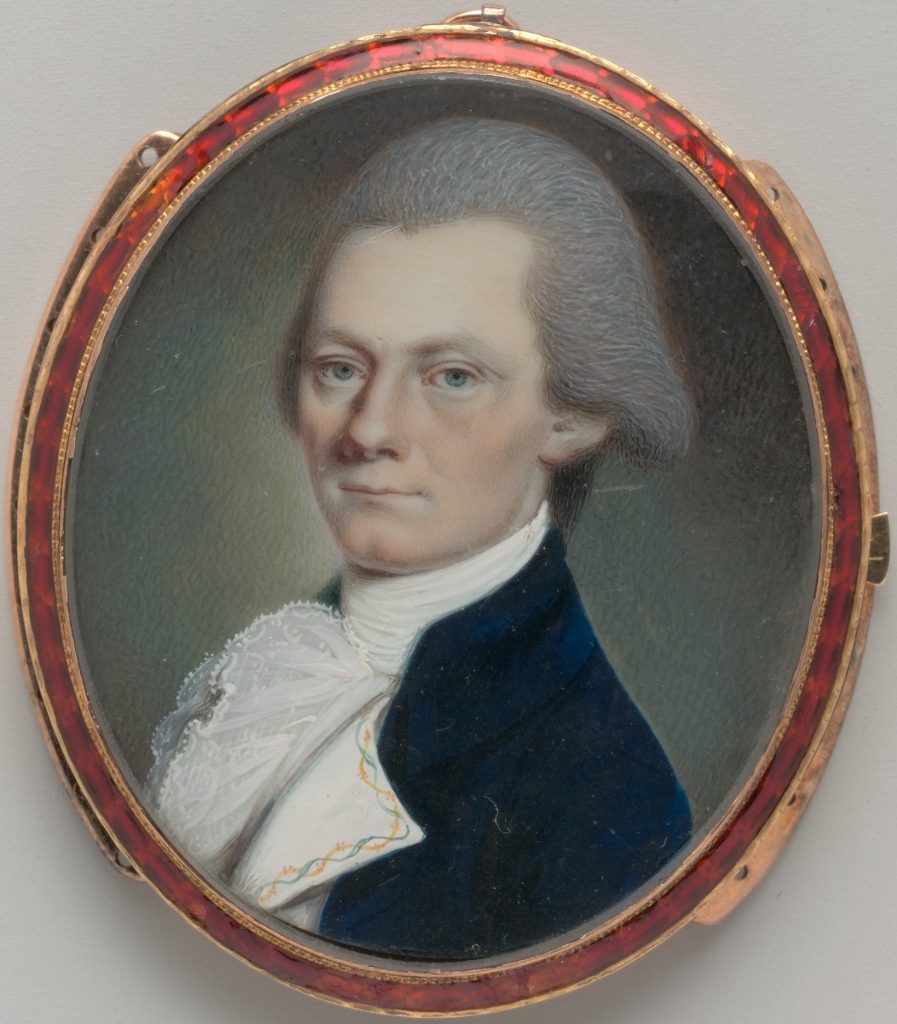

William Few (Wiki Image).
William Few of Georgia faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Few was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Few had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Few was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Few was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Georgia.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Few helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
- Served as a United States Senator from Georgia. Few served as a United States Senator from Georgia from 1789 to 1793. He was a strong advocate for the Constitution and for the principles of federalism.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Few knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Few understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Few believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Few served as a United States Senator from Georgia from 1789 to 1793. He was a strong advocate for the Constitution and for the principles of federalism.
Few’s work on the Constitution and his service as a United States Senator had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
William Few was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Few was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as a United States Senator and was a strong advocate for the Constitution and the principles of federalism.
Few’s legacies are a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Baldwin, Abraham, Ga., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom, concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
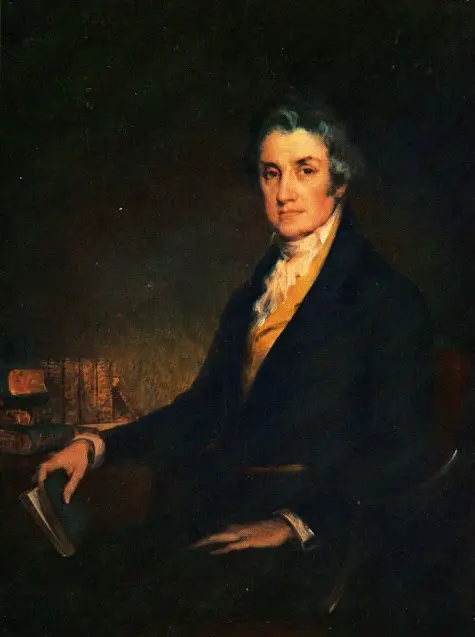

Abraham Baldwin (Wiki Image).
Abraham Baldwin of Georgia faced the following obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution:
Obstacles
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. Baldwin was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He had to balance these competing interests in order to build consensus among the delegates.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states. Some delegates feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states. Baldwin had to convince these delegates that the Constitution would protect the rights of the states.
- Opposition from delegates who wanted to strengthen the institution of slavery. Baldwin was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He had to balance his personal views with the political realities of the time.
Successes
- Played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. Baldwin was one of the most influential delegates to the Constitutional Convention. He helped to draft several important provisions of the Constitution, including the Supremacy Clause and the Commerce Clause. He also played a key role in securing the ratification of the Constitution in Georgia.
- Helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced. The Constitution that Baldwin helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years. It is a government that is both strong enough to govern effectively and balanced enough to protect the rights of individuals and states.
- Established the University of Georgia. In 1785, Baldwin drafted the charter for the University of Georgia, which became the first public university in the United States. He also served as the university’s first president.
Wisdom
- Understood the importance of compromise. Baldwin knew that compromise was essential to creating a Constitution that would be acceptable to all of the states. He was willing to compromise on his own views in order to reach a consensus among the delegates.
- Believed that the Constitution should be a living document. Baldwin understood that the Constitution would need to be amended over time to meet the changing needs of the country. He supported the inclusion of an amendment process in the Constitution.
- Was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals. Baldwin believed that the rule of law was essential for a just and orderly society. He also believed that the rights of individuals should be protected by the government.
Led the government in the past and future
Baldwin served as a United States Senator from Georgia from 1793 to 1799. He also served as the president of the University of Georgia from 1785 to 1801.
Baldwin’s work on the Constitution, his service as a United States Senator, and his founding of the University of Georgia had a significant impact on the development of the United States government. He is considered to be one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Conclusion
Abraham Baldwin was a complex and fascinating figure. He was a slave owner, but he also had reservations about slavery. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, but he also had concerns about the power of the central government.
Despite his flaws, Baldwin was a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring. He played a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution, and he helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. He also served as a United States Senator and founded the University of Georgia, both of which had a significant impact on the development of the country.
Baldwin’s legacy is a complex one, but he is undoubtedly one of the most important figures in American history.
A.I. Langdon, John, N.H., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
John Langdon (Wiki Image).
John Langdon (1741-1819) was a Founding Father of the United States and a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787 from New Hampshire. He was a wealthy merchant and a successful politician. He served as Governor of New Hampshire and as a United States Senator.
Langdon was born in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. He was a successful merchant and a member of the New Hampshire Provincial Assembly. He served in the Continental Army during the American Revolution and was a member of the New Hampshire delegation to the Continental Congress.
Langdon was a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787. He was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He played a key role in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
Langdon was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations. He returned to New Hampshire and worked tirelessly for the ratification of the Constitution. He was a member of the New Hampshire Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
New Hampshire was the ninth state to ratify the Constitution, and Langdon played a key role in securing its ratification. He was a true Founding Father of the United States, and his contributions to the country are significant and enduring.
Obstacles
Langdon faced some opposition from delegates who wanted to create a weaker central government. He also faced opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states and who feared that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states.
Successes
Langdon was able to overcome these obstacles and play a key role in the drafting and ratification of the Constitution. He was also able to build consensus among the delegates and help to create a government that was both strong and balanced.
Wisdom
Langdon understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all. He also believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed. He was also a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Led the government in the past and future
While Langdon did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution had a profound impact on the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that Langdon helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- Langdon’s work on the Constitution also helped to establish many of the precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
In that sense, Langdon can be said to have led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Examples of Langdon’s leadership
- Langdon was a key player in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Langdon also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in New Hampshire. He was a member of the New Hampshire Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
- Langdon served as Governor of New Hampshire from 1788 to 1789 and from 1805 to 1809. He also served as a United States Senator from 1801 to 1811.
Impact of Langdon’s leadership on the government in the past and future
Langdon’s work on the Constitution helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Great Compromise, which Langdon played a key role in drafting, ensured that the federal government would have enough power to govern effectively while also protecting the rights of the states.
Langdon’s belief in the importance of compromise and in the need for a living Constitution has continued to guide the United States government. The Constitution has been amended 27 times since it was first ratified, and each amendment has reflected the changing needs of the country.
Langdon’s legacy can also be seen in the Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has often cited Langdon’s arguments in cases involving states’ rights and the individual rights protected by the Constitution.
Overall, John Langdon was a Founding Father who played a key role in shaping the United States government. His legacy continues to be felt today, and his contributions to the Constitution have helped to create a government that is both strong and free.
A.I. Gilman, Nicholas, N.H., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Nicholas Gilman Jr. (Wiki Image).
Nicholas Gilman (1755-1814) was a Founding Father of the United States and a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787 from New Hampshire. He was a strong supporter of the Constitution, and he played a key role in its ratification in New Hampshire.
Gilman was born in Exeter, New Hampshire. He was a successful merchant and a member of the New Hampshire Provincial Assembly. He served in the Continental Army during the American Revolution and was a member of the New Hampshire delegation to the Continental Congress.
Gilman was a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787. He was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights. He played a key role in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
Gilman was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations. He returned to New Hampshire and worked tirelessly for the ratification of the Constitution. He was a member of the New Hampshire Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
New Hampshire was the ninth state to ratify the Constitution, and Gilman played a key role in securing its ratification. He was a true Founding Father of the United States, and his contributions to the country are significant and enduring.
Here are some specific examples of Gilman’s leadership:
- He was a strong supporter of the Constitution and played a key role in its ratification in New Hampshire.
- He was a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787 and played a key role in the drafting of the Great Compromise.
- He served as a member of the New Hampshire Provincial Assembly, the Continental Army, and the Continental Congress.
Gilman’s work helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Constitution that he helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
Gilman’s legacy continues to be felt today. His belief in the importance of a strong central government and states’ rights continues to be a guiding principle of the American government.
A.I. Livingston, William, N.J., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

William Livingston (Wiki Image).
Yes, I can provide more information about William Livingston, N.J.
William Livingston (1723-1790) was a Founding Father of the United States and the first Governor of New Jersey. He was a strong advocate for states’ rights and republican government. He also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in New Jersey.
Livingston was born in Albany, New York. He studied law at Yale College and was admitted to the bar in 1745. He practiced law in New York City and Albany before moving to New Jersey in 1772.
Livingston quickly became a leader in New Jersey politics. He was elected to the New Jersey Provincial Congress in 1774 and served as its president in 1775. He was also a member of the Continental Congress from 1774 to 1776.
Livingston was a strong supporter of the American Revolution. He wrote numerous essays and articles in support of the war, and he served as a delegate to the Continental Congress that signed the Declaration of Independence.
In 1776, Livingston was elected the first Governor of New Jersey. He served as Governor until his death in 1790.
Livingston was a strong advocate for states’ rights and republican government. He believed that the federal government should have limited powers and that the states should retain most of their sovereignty. He also believed that the people should have a direct say in government through elections.
Livingston played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in New Jersey. He was a member of the New Jersey Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution. He argued that the Constitution was necessary to create a strong central government that could protect the United States from foreign aggression and promote economic prosperity.
Livingston was a complex and controversial figure. He was a brilliant lawyer and a gifted writer. He was also a passionate advocate for his beliefs. He was a true Founding Father of the United States, and his contributions to the country are significant and enduring.
Here are some specific examples of Livingston’s leadership:
- He was a strong advocate for states’ rights and republican government.
- He played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in New Jersey.
- He served as the first Governor of New Jersey from 1776 to 1790.
Livingston’s work helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Constitution that he helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
Livingston’s legacy continues to be felt today. His belief in the importance of states’ rights and republican government continues to be a guiding principle of American government.
A.I. Paterson, William, N.J., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
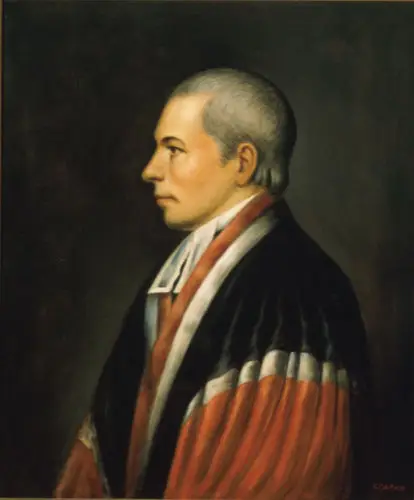

William Paterson (Wiki Image).
William Paterson, N.J., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
Obstacles
- Paterson faced opposition from delegates who wanted to create a strong central government. He was a strong advocate for states’ rights, and he believed that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states.
- Paterson was also a critic of slavery, but he was unable to convince the Convention to abolish it.
- Paterson was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Paterson was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Paterson was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Paterson understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was also a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Led the government in the past and future
While Paterson did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution had a profound impact on the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that Paterson helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- Paterson’s work on the Constitution also helped to establish many of the precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
In that sense, Paterson can be said to have led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Here are some specific examples of Paterson’s leadership:
- Paterson was a key player in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Paterson also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in New Jersey. He was a member of the New Jersey Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Paterson also served as Governor of New Jersey and as a Justice of the Supreme Court. He was a successful lawyer and a respected public figure.
Paterson was a complex and controversial figure, but he was also a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring.
How Paterson’s leadership impacted the government in the past and future:
Paterson’s work on the Constitution helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Great Compromise, which Paterson played a key role in drafting, ensured that the federal government would have enough power to govern effectively while also protecting the rights of the states.
Paterson’s belief in the importance of compromise and in the need for a living Constitution has continued to guide the United States government. The Constitution has been amended 27 times since it was first ratified, and each amendment has reflected the changing needs of the country.
Paterson’s legacy can also be seen in the Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has often cited Paterson’s arguments in cases involving states’ rights and the individual rights protected by the Constitution.
Overall, William Paterson was a Founding Father who played a key role in shaping the United States government. His legacy continues to be felt today, and his contributions to the Constitution have helped to create a government that is both strong and free.
A.I. Mifflin, Thomas, Pa., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Thomas Mifflin (Wiki Image).
Thomas Mifflin, a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787 from Pennsylvania, faced obstacles, achieved successes, and demonstrated wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
Obstacles
- Mifflin faced opposition from delegates who wanted to create a strong central government. He was a strong advocate for states’ rights, and he believed that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states.
- Mifflin was also a critic of slavery, but he was unable to convince the Convention to abolish it.
- Mifflin was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Mifflin was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Mifflin was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Mifflin understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended.
- He was also a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Led the government in the past and future
While Mifflin did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution profoundly impacted the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that Mifflin helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- Mifflin’s work on the Constitution also helped establish many precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
In that sense, Mifflin has led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Here are some specific examples of Mifflin’s leadership:
- Mifflin was a key player in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Mifflin also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in Pennsylvania. He was a member of the Pennsylvania Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Mifflin also served as the President of the Continental Congress and as the first Governor of Pennsylvania. He was a successful merchant and a respected public figure.
Mifflin was a complex and controversial figure, but he was also a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring.
How Mifflin’s leadership impacted the government in the past and future
Mifflin’s work on the Constitution helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Great Compromise, which Mifflin played a key role in drafting, ensured that the federal government would have enough power to govern effectively while also protecting the rights of the states.
Mifflin’s belief in the importance of compromise and in the need for a living Constitution has continued to guide the United States government. The Constitution has been amended 27 times since it was first ratified, and each amendment has reflected the country’s changing needs.
Mifflin’s legacy can also be seen in the Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has often cited Mifflin’s arguments in cases involving states’ and individual rights protected by the Constitution.
Overall, Thomas Mifflin was a Founding Father who played a key role in shaping the United States government. His legacy continues to be felt today, and his contributions to the Constitution have helped create a strong and free government.
A.I. Clymer, George, Pa., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

George Clymer (Wiki Image).
George Clymer, a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787 from Pennsylvania, faced obstacles, achieved successes, and demonstrated wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
Obstacles
- Clymer faced opposition from delegates who wanted to create a strong central government. He was a strong advocate for states’ rights, and he believed that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states.
- Clymer was also a critic of slavery, but he was unable to convince the Convention to abolish it.
- Clymer was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Clymer was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Clymer was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Clymer understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was also a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Led the government in the past and future
While Clymer did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution profoundly impacted the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that Clymer helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- Clymer’s work on the Constitution also helped establish many precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
In that sense, Clymer can be said to have led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Here are some specific examples of Clymer’s leadership:
- Clymer was a key player in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Clymer also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in Pennsylvania. He was a member of the Pennsylvania Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Clymer also served as a member of the Continental Congress and as a U.S. Representative. He was a successful merchant and a respected public figure.
Clymer was a complex and controversial figure, but he was also a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring.
How Clymer’s leadership impacted the government in the past and future
Clymer’s work on the Constitution helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Great Compromise, which Clymer played a key role in drafting, ensured that the federal government would have enough power to govern effectively while also protecting the rights of the states.
Clymer’s belief in the importance of compromise and in the need for a living Constitution has continued to guide the United States government. The Constitution has been amended 27 times since it was first ratified, and each amendment has reflected the changing needs of the country.
Clymer’s legacy can also be seen in the Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has often cited Clymer’s arguments in cases involving states’ rights and the individual rights protected by the Constitution.
Overall, George Clymer was a Founding Father who played a key role in shaping the United States government. His legacy continues to be felt today, and his contributions to the Constitution have helped to create a government that is both strong and free.
A.I. FitzSimons, Thomas, Pa., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Thomas Fitzsimons (Wiki Image).
Thomas FitzSimons, a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787 from Pennsylvania, faced obstacles, achieved successes, and demonstrated wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
Obstacles
- FitzSimons faced opposition from delegates who favored a strong central government.
- He was also an immigrant, and he faced opposition from delegates who wanted to restrict immigrants’ rights.
- FitzSimons was a merchant, and he faced opposition from delegates who wanted to restrict the power of the business community.
Successes
- FitzSimons was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- FitzSimons was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- FitzSimons understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was also a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Led the government in the past and future
While FitzSimons did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution had a profound impact on the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that FitzSimons helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- FitzSimons’ work on the Constitution also helped to establish many of the precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
In that sense, FitzSimons has led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Here are some specific examples of FitzSimons’ leadership:
- FitzSimons was a key player in drafting the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- FitzSimons also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in Pennsylvania. He was a member of the Pennsylvania Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, FitzSimons also served as a member of the Continental Congress and as a U.S. Representative. He was a successful merchant and a respected public figure.
FitzSimons was a complex and controversial figure, but he was also a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring.
How FitzSimons’ leadership impacted the government in the past and future
FitzSimons’ work on the Constitution helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Great Compromise, which FitzSimons played a key role in drafting, ensured that the federal government would have enough power to govern effectively while also protecting the rights of the states.
FitzSimons’ belief in the importance of compromise and in the need for a living Constitution has continued to guide the United States government. The Constitution has been amended 27 times since it was first ratified, and each amendment has reflected the changing needs of the country.
FitzSimons’ legacy can also be seen in the Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has often cited FitzSimons’ arguments in cases involving states’ rights and the individual rights protected by the Constitution.
Overall, Thomas FitzSimons was a Founding Father who played a key role in shaping the United States government. His legacy continues to be felt today, and his contributions to the Constitution have helped to create a government that is both strong and free.
A.I. Ingersoll, Jared, Pa., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

Jared Ingersoll (Wiki Image).
Jared Ingersoll, a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787 from Pennsylvania, faced obstacles, achieved successes, and demonstrated wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
Obstacles
- Ingersoll faced opposition from delegates who wanted to create a strong central government. He was a strong advocate for states’ rights, and he believed that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states.
- Ingersoll was also a vocal opponent of slavery, but he was unable to convince the Convention to abolish it.
- Ingersoll was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Ingersoll was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Ingersoll was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Ingersoll understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was also a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Led the government in the past and future
While Ingersoll did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution had a profound impact on the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that Ingersoll helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- Ingersoll’s work on the Constitution also helped establish many precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
Ingersoll can be said to have led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Here are some specific examples of Ingersoll’s leadership:
- Ingersoll was a key player in drafting the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Ingersoll also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in Pennsylvania. He was a member of the Pennsylvania Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Ingersoll also served as Attorney General of Pennsylvania, U.S. District Attorney for Pennsylvania, and Attorney General of the United States. He was a successful lawyer and a respected public figure.
Ingersoll was a complex and controversial figure, but he was also a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring.
How Ingersoll’s leadership impacted the government in the past and future
Ingersoll’s work on the Constitution helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Great Compromise, which Ingersoll played a key role in drafting, ensured that the federal government would have enough power to govern effectively while also protecting the rights of the states.
Ingersoll’s belief in the importance of compromise and in the need for a living Constitution has continued to guide the United States government. The Constitution has been amended 27 times since it was first ratified, and each amendment has reflected the changing needs of the country.
Ingersoll’s legacy can also be seen in the Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has often cited Ingersoll’s arguments in cases involving states’ rights and the individual rights protected by the Constitution.
Overall, Jared Ingersoll was a Founding Father who played a key role in shaping the United States government. His legacy continues to be felt today, and his contributions to the Constitution have helped to create a government that is both strong and free.
A.I. Bedford, Gunning, Jr., Del., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
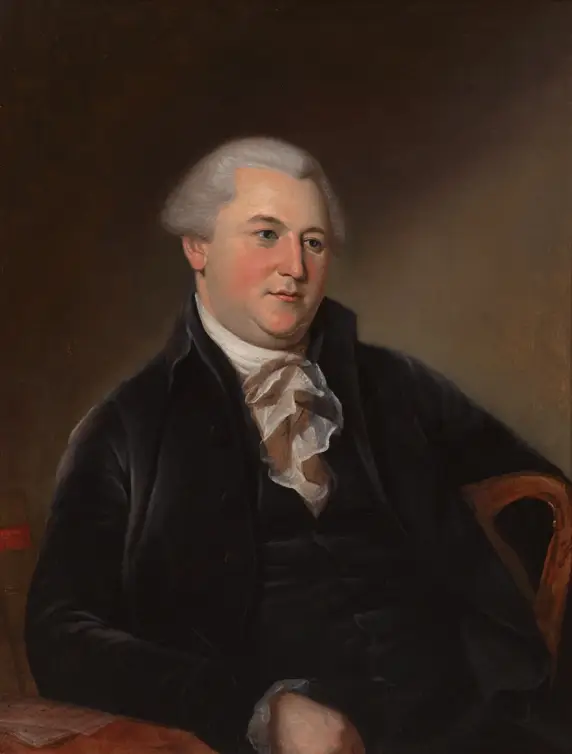

Gunning Bedford Jr. (Wiki Image).
Gunning Bedford, Jr., Del., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
Obstacles
- Bedford faced opposition from delegates who wanted to create a strong central government. He was a strong advocate for states’ rights, and he believed that a strong central government would pose a threat to the states.
- Bedford was also a vocal opponent of slavery, but he was unable to convince the Convention to abolish it.
- Bedford was a Federalist, but he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Bedford was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Bedford was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Bedford understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was also a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Led the government in the past and future
While Bedford did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution had a profound impact on the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that Bedford helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- Bedford’s work on the Constitution also helped to establish many of the precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
In that sense, Bedford can be said to have led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Here are some specific examples of Bedford’s leadership:
- Bedford was a key player in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Bedford also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in Delaware. He was a member of the Delaware Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Bedford also served as a member of the Continental Congress and as a judge on the Delaware Supreme Court. He was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
How Bedford’s leadership impacted the government in the past and future
Bedford’s work on the Constitution helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Great Compromise, which Bedford played a key role in drafting, ensured that the federal government would have enough power to govern effectively while also protecting the rights of the states.
Bedford’s belief in the importance of compromise and in the need for a living Constitution has continued to guide the United States government. The Constitution has been amended 27 times since it was first ratified, and each amendment has reflected the changing needs of the country.
Bedford’s legacy can also be seen in the Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has often cited Bedford’s arguments in cases involving states’ rights and the individual rights protected by the Constitution.
Overall, Gunning Bedford, Jr. was a Founding Father who played a key role in shaping the United States government. His legacy continues to be felt today, and his contributions to the Constitution have helped to create a government that is both strong and free.
A.I. Brearley, David, N.J., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

David Brearley (Wiki Image).
Brearley, David, N.J., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
Obstacles
- David Brearley faced opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- He was also a critic of slavery, but he was unable to convince the Convention to abolish it.
- Brearley was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Brearley was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Brearley was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Brearley understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was a master of legal argument and was able to persuade his colleagues to adopt his proposals.
Led the government in the past and future
David Brearley led the government in the past and future by helping to create the Constitution. The Constitution is the foundation of the United States government, and it has served the country well for over 200 years. Brearley’s wisdom and foresight continue to guide the United States government today.
Specifically, Brearley’s work on the Constitution helped to establish the following principles:
- The separation of powers between the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government.
- The system of checks and balances prevents any one branch of government from becoming too powerful.
- The principle of federalism divides power between the federal government and the state governments.
- The protection of individual rights, such as the right to freedom of speech, religion, and assembly.
These principles are essential to the American system of government, and they continue to shape the way that the United States government is run today.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Brearley also served as Chief Justice of the New Jersey Supreme Court and as a member of the United States House of Representatives. He was a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Brearley was a complex and controversial figure, but he was also a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring.
A.I. Dickinson, John, Del., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

John Dickinson (Wiki Image).
John Dickinson was a delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787 from Delaware. He was a moderate who favored a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights.
Obstacles
- Dickinson faced opposition from delegates who wanted to create a very strong central government.
- He was also opposed by delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Dickinson was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Dickinson was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Dickinson was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Dickinson understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was a master of legal argument and was able to persuade his colleagues to adopt his proposals.
Led the government in the past and future
While Dickinson did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution had a profound impact on the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that Dickinson helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- Dickinson’s work on the Constitution also helped to establish many of the precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
In that sense, Dickinson can be said to have led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Here are some specific examples of Dickinson’s leadership:
- Dickinson was a key player in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Dickinson also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in Delaware. He was the author of the “Fabius” letters, which were published in newspapers and helped to convince Delawareans to support the Constitution.
- Dickinson’s work on the Constitution helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced, and his legacy continues to be felt today.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Dickinson also served as President of Delaware and as a member of the Continental Congress. He was a strong advocate for American independence and for a strong federal government.
Dickinson was a complex and controversial figure, but he was also a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring.
A.I. Blair, John, Va., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.

John Blair Jr. (Wiki Image).
John Blair was a delegate to the U.S. Constitutional Convention of 1787 from Virginia. He was a strong advocate for states’ rights, but he also believed in the importance of a strong central government.
Obstacles
- Blair faced opposition from delegates who wanted to create a strong central government.
- He was also a slave owner, and he faced opposition from delegates who wanted to abolish slavery.
- Blair was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Blair was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Blair was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Blair understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was a master of legal argument and was able to persuade his colleagues to adopt his proposals.
Led the government in the past and future
While Blair did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution and the Supreme Court had a profound impact on the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that Blair helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- Blair’s work on the Constitution also helped to establish many of the precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
- As an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court, Blair wrote many important opinions that helped to define the scope of federal power and the rights of individuals.
- His opinions continue to be cited by the Supreme Court today.
In that sense, Blair can be said to have led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Here are some specific examples of Blair’s leadership:
- Blair was a key player in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Blair also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in Virginia. He lobbied members of the Virginia Ratifying Convention and wrote articles in support of the Constitution.
- As an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court, Blair wrote many important opinions that helped to define the scope of federal power and the rights of individuals. For example, in the case of Hylton v. United States (1796), Blair wrote the majority opinion that struck down a federal tax on carriages. In the case of Chisholm v. Georgia (1793), Blair wrote the majority opinion that allowed citizens of one state to sue another state in federal court.
Blair’s leadership on the Constitution and the Supreme Court had a profound impact on the development of the United States government. His work helped to create a government that is both strong and balanced, and his legacy continues to be felt today.
A.I. Broom, Jacob, Del., faced obstacles, successes, and wisdom concerning the Constitution. He led the government in the past and future.
Jacob Broom was a delegate to the Constitutional Convention of 1787 from Delaware. He was a strong supporter of a strong central government, but he also believed in the importance of states’ rights.
Obstacles
- Broom faced opposition from delegates who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- He was also a critic of slavery, but he was unable to convince the Convention to abolish it.
- Broom was a Federalist, and he faced opposition from Anti-Federalists, who opposed the Constitution.
Successes
- Broom was a member of the Committee of Detail, which was responsible for drafting the first version of the Constitution.
- He also played a key role in the debate over the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Broom was one of the few delegates who signed the Constitution without reservations.
Wisdom
- Broom understood the importance of compromise in order to create a Constitution that would be acceptable to all.
- He believed that the Constitution should be a living document that could be amended as needed.
- He was also a strong advocate for the rule of law and for the rights of individuals.
Led the government in the past and future
While Broom did not hold a formal position as head of state or government, his work on the Constitution had a profound impact on the development of the United States government.
- The Constitution that Broom helped to draft has served as the foundation of the United States government for over 200 years.
- Broom’s work on the Constitution also helped to establish many of the precedents that the Supreme Court still follows today.
In that sense, Broom can be said to have led the government in the past and future by helping to shape the way that the Constitution is interpreted and applied.
Here are some specific examples of Broom’s leadership:
- Broom was a key player in the drafting of the Great Compromise, which resolved the debate between those who wanted a strong central government and those who wanted to preserve the power of the states.
- Broom also played a key role in the ratification of the Constitution in Delaware. He was a member of the Delaware Ratifying Convention, and he spoke in favor of the Constitution.
In addition to his work on the Constitution, Broom also served in the Delaware General Assembly and as a postmaster. He was a successful businessman and a respected civic leader.
Broom was a complex and controversial figure, but he was also a man of great wisdom and foresight. His contributions to the United States government are significant and enduring.
How Broom’s leadership impacted the government in the past and future
Broom’s work on the Constitution helped to create a government that was both strong and balanced. The Great Compromise, which Broom played a key role in drafting, ensured that the federal government would have enough power to govern effectively while also protecting the rights of the states.
Broom’s belief in the importance of compromise and in the need for a living Constitution has continued to guide the United States government. The Constitution has been amended 27 times since it was first ratified, and each amendment has reflected the changing needs of the country.
Broom’s legacy can also be seen in the Supreme Court’s interpretation of the Constitution. The Supreme Court has often cited Broom’s arguments in cases involving states’ rights and the individual rights protected by the Constitution.
Overall, Jacob Broom was a Founding Father who played a key role in shaping the United States government. His legacy continues to be felt today, and his contributions to the Constitution have helped to create a government that is both strong and free.
A.I. Jackson, William, Secretary Constitution.

William Jackson (Wiki Image).
William Jackson was a secretary of the Constitutional Convention of 1787. He was responsible for keeping detailed records of the Convention’s debates, which have been invaluable to historians and legal scholars. He also helped to draft the final version of the Constitution.
Jackson was a skilled writer and administrator, and he played an important role in the drafting of the Constitution. He was also a strong advocate for the ratification of the Constitution.
Jackson was born in England in 1759 and emigrated to the American colonies in 1774. He served in the Continental Army during the American Revolution, and he was also a secretary to General George Washington.
After the war, Jackson worked as a lawyer and a journalist. He was also a member of the Pennsylvania State House of Representatives.
Jackson was elected as a secretary of the Constitutional Convention in 1787. He was one of only two people to keep detailed records of the Convention’s debates. His records have been invaluable to historians and legal scholars, and they have helped to shed light on the intentions of the Founding Fathers.
Jackson also helped to draft the final version of the Constitution. He worked closely with the Founding Fathers to ensure that the document was clear and concise.
After the Constitutional Convention, Jackson was a strong advocate for the ratification of the Constitution. He wrote articles and gave speeches in support of the document.
Jackson died in 1828. He is remembered as one of the Founding Fathers of the United States and for his important role in the drafting of the Constitution.



